Étant donné un nombre n, trouvez toutes les séquences binaires de longueur 2n telles que la somme des n premiers bits soit la même que la somme des n derniers bits.
Exemples :
ordre aléatoire SQL
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
L'idée est de corriger le premier et le dernier bits, puis de se reproduire pour les 2*(n-1) bits restants. Il existe quatre possibilités lorsque nous corrigeons le premier et le dernier bits :
- Le premier et le dernier bits sont 1, les n - 1 bits restants des deux côtés doivent également avoir la même somme.
- Le premier et le dernier bits sont 0, les n - 1 bits restants des deux côtés doivent également avoir la même somme.
- Le premier bit est 1 et le dernier bit est 0. La somme des n-1 bits restants sur le côté gauche doit être inférieure de 1 à la somme des n-1 bits sur le côté droit.
- Le premier bit est 0 et le dernier bit est 1. La somme des n-1 bits restants sur le côté gauche doit être 1 de plus que la somme des n-1 bits sur le côté droit.
Vous trouverez ci-dessous la mise en œuvre de l’idée ci-dessus –
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include
// Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char out[] int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { System.out.print(out); System.out.print(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void main (String[] args) { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array out[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences(diff out start end): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2): return; # if all bits are filled if (start > end): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if (diff == 0): print(''.join(list(out))end=' '); return; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # Driver program # input number n = 2; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out=['']*(2*n); findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); # This code is contributed by mits
// C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char []outt int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { Console.Write(outt); Console.Write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences($diff $out $start $end) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2)) return; // if all bits are filled if ($start > $end) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ($diff == 0) print(implode(''$out).' '); return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out[$start] = '0'; $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out[$start] = '1'; $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out=array_fill(02*$n''); findAllSequences(0 $out 0 2*$n - 1); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?> <script> // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences(diff outt start end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2 10)) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { document.write(outt.join('')); document.write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // input number let n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1); // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); </script>
Sortir
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Complexité temporelle : O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N à cause de 4 appels récursifs et N (simplifié à partir de 2N) pour le temps passé à imprimer des chaînes de taille 2N
Espace auxiliaire : SUR)
Il existe une autre approche par laquelle nous générons toutes les chaînes possibles de longueur n et les stockons dans une liste à un index représentant leur somme. Ensuite, nous parcourons chaque liste et générons les chaînes de taille 2n en imprimant chaque chaîne avec toutes les autres chaînes de la liste totalisant la même valeur.
C++// C++ program to implement the approach #include
// Java program to implement the approach import java.util.*; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences(int n) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.add( new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum( n sumToString new ArrayList<String>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum( int n ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString ArrayList<String> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if (n == 0) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = ''; for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) { seq = seq + sequence.get(i); } ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar); x.add(seq); sumToString.set(sumSoFar x); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.remove(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1); sequence.remove(0); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences( ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for (int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) { // Append for (int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence1++) { for (int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence2++) { if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1) { System.out.print('1111'); } else { System.out.println( sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence1) + sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence2)); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call findAllSequences(2); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
def findAllSequences(n): sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0) permuteSequences(sumToString) def generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0: sumToString[sumSoFar].append(''.join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence.append('0') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar) sequence.pop() #Generate sequence +1 sequence.append('1') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1) sequence.pop() def permuteSequences(sumToString): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString: # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr: for sequence2 in sumIndexArr: print(sequence1 + sequence2) findAllSequences(2) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { static void findAllSequences(int n) { List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>(); for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString new List<string>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n List<List<string>> sumToString List<string> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = ''; for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++) { seq = seq + sequence[i]; } sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.Add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.RemoveAt(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.Add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.RemoveAt(0); } static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++) { for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1) { Console.Write('1111'); } else { Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]); } } } } } static void Main() { findAllSequences(2); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
<script> function findAllSequences(n) { let sumToString = []; for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } function generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join('')); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.push('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.shift(); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.push('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.shift(); } function permuteSequences(sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++) { for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1) { document.write('1111'); } else { document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + ''); } } } } } findAllSequences(2); // This code is contributed by decode2207. </script>
Sortir
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Analyse de la complexité temporelle :
générer des séquences avec la somme = O((2N)*N)
- 2N: nous générons toutes les permutations de chaînes binaires de taille N
- N : convertit la liste de caractères en chaîne et la stocke dans un tableau. Cela se fait dans le cas de base.
permuteSéquences = O((2N) *N!/(N/2)!2*N)
- 2N : nous parcourons toute la chaîne générée de taille n
- N!/(N/2)!2: Celui-ci est un peu difficile à expliquer
prenons N = 2 comme exemple. Notre tableau de séquences possibles de taille n serait :
| indice de tableau | 1 | 2 | |
| liste de chaînes | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
Dans la liste des chaînes dont l'index représente la somme, nous obtenons le nombre de chaînes de taille 2n en utilisant la formule « n choisir k ». Dans notre cas, ce serait nCk *nCk où k représente le nombre de 1 dans chaque moitié de la chaîne de taille 2n :
k = 0 nous avons (2C0)^2 = 1 chaîne (0000)
k = 1 nous avons (2C1)^2 chaîne = 4 chaînes (0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 nous avons (2c2)^2 = 1 chaîne (1111)
tutoriel javascript
Nous obtenons notre plus longue liste de chaînes lorsque k = N/2 doncNCN/2= N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2) !] ce qui simplifieNCN/2= N!/(N/2)!2
Par conséquent, pour chaque élément, nous devons parcourir au maximumNCN/2pour former des chaînes de longueur 2N
Sans preuve formelle si on représente graphiquement 2^N et N!/(N/2)!2on voit que 2Na un taux de croissance plus rapide que ce dernier. Donc O(2N*N!/(N/2)2)< O(2N*2N) = O(22n) = O(4N)
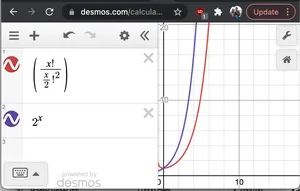 Graphique de 2^x et nC(n/2)
Graphique de 2^x et nC(n/2)- N : il faut imprimer chaque chaîne de taille 2N
Enfin, nous pouvons ignorer la complexité temporelle de generateSequencesWithSum car permuteSequence est le terme principal.
Complexité temporelle : O(2N*N!/(N/2)!2* N) (mieux que la première solution de O((4^N) * N voir l'explication ci-dessus pour plus de détails)
Espace auxiliaire :O(2N) car nous stockons toutes les permutations de chaînes binaires de taille N
annotations dans Spring Boot
#include
import java.util.*; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data; int sum; FirstHalf(String data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map<Integer ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); //first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new ArrayList<>(); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString(String s) { int sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(char c: s.toCharArray()) { sum += c - '0'; } return sum; } public static void perm(String p char[] bin int level int n) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if(level == 0) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map.putIfAbsent(sum new ArrayList<String>()); map.get(sum).add(p); return; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(char c: bin) { perm(p+c bin level-1 n); } } public static void result() { int i = 0; for(FirstHalf first: firstHalf) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList<String> secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(String second: secondHalf) { //append first and second half and print System.out.print(first.data+second+' '); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) System.out.println(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { char[] up = {'0' '1'}; int n = 2; perm('' up n n); result(); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
# Python code implementation class FirstHalf: def __init__(self data sum): self.data = data self.sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString(s): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range(len(s)): sum += ord(s[i]) - ord('0') return sum def perm(p bin level n): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0: # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString(p) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.append(FirstHalf(p sum)) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map: map[sum] = [] map[sum].append(p) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range(len(bin)): perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n) def result(): i = 0 for j in range(len(firstHalf)): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf[j].sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map[sum] for k in range(len(secondHalf)): # append first and second half and print print(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' ' end='') # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if(i % 6 == 0): print('n') up = ['0' '1'] n = 2 perm('' up n n) result() # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class FirstHalf { public string data; public int sum; public FirstHalf(string data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary<int List<string>> mp = new Dictionary<int List<string>>(); // first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new List<FirstHalf>(); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString(string s) { int sum = 0; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach (char c in s) { sum += (c - '0'); } return sum; } static void perm(string p char[] bin int level int n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if (level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.Add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if (mp.ContainsKey(sum)) { mp[sum].Add(p); } else { mp.Add(sum new List<string> { p }); } return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = bin[i]; perm(p + c bin level - 1 n); } } static void result() { int i = 0; foreach (FirstHalf first in firstHalf) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List<string> secondHalf = mp[sum]; foreach (string second in secondHalf) { // append first and second half and print Console.Write(first.data + second + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if (i % 6 == 0) Console.WriteLine(); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { char[] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2; string x = ''; perm(x up n n); result(); } }
class FirstHalf { constructor(data sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map(); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString(s) { let sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { sum += s.charCodeAt(i) - '0'.charCodeAt(0); } return sum; } function perm(p bin level n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if(level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.push(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if(!map.has(sum)) map.set(sum []); map.get(sum).push(p); return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(let i = 0; i < bin.length; i++) { perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n); } } function result() { let i = 0; for(let j = 0; j < firstHalf.length; j++) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf[j].sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(let k = 0; k < secondHalf.length; k++) { // append first and second half and print process.stdout.write(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) process.stdout.write('n'); } } } const up = ['0' '1']; const n = 2; perm('' up n n); result();
Sortir
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algorithme:
1. Générez toutes les permutations binaires de taille n
2. Calculez la somme des bits de chaque permutation et mémorisez-la pour la seconde moitié
[par exemple : pour n=2, rappelez-vous qu'il y a deux chaînes avec sum = 1, c'est-à-dire '01' '10' ]
3. Itérer toutes les permutations générées et pour chacune d'elles ajouter la seconde moitié en fonction de la somme des bits
Analyse de la complexité temporelle :
Java concaténation de chaînes
sommeDeChaîne() = O(N) : parcourez chaque bit et ajoutez-le à la somme
permanente() = O(2N*N)
2N * N : nous générons toutes les permutations de bits binaires de taille N et trouvons la somme des bits pour chaque permutation
résultat() = O((2N) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2N : nous parcourons toutes les permutations possibles de taille N (première moitié)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2: (taille maximale de la seconde moitié) : explication ci-dessous :
prenons N = 4 comme exemple.:
//Hash-Map ressemble à
0 -> [0000] ................................(taille de la liste : 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................(taille de la liste : 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................(taille de la liste : 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................(taille de la liste : 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................(taille de la liste : 4C4 = 1)
On observe ici que chaque liste a une taille de N choisissez Clé qui sera maximale à N choisissez N/2
Puisque nous réitérons tous les 2Npermutations et ajout de la seconde moitié de la carte. La carte a la liste de taille maximale à la position N/2.
Le pire des cas se produit en position N/2 où nous devons traverser NCN/2 = N!/(N/2) !2permutations.
convention de dénomination pour Java
Complexité temporelle : O(2N*N!/(N/2)!2)
Espace auxiliaire : O(2N) parce que nous stockons toutes les permutations de chaînes binaires de taille N
