Arbre AVL :
L'arbre AVL est un arbre de recherche binaire auto-équilibré ( BST ) où la différence entre les hauteurs des sous-arbres gauche et droit ne peut pas être supérieure à un pour tous les nœuds.
Exemple d'arborescence AVL :
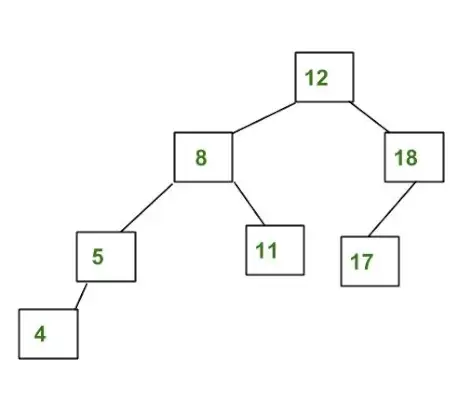
L'arbre ci-dessus est AVL car les différences entre les hauteurs des sous-arbres gauche et droit pour chaque nœud sont inférieures ou égales à 1.
Exemple d'arbre qui n'est PAS un arbre AVL :

L'arbre ci-dessus n'est pas AVL car les différences entre les hauteurs des sous-arbres gauche et droit pour 8 et 12 sont supérieures à 1.
Pourquoi les arbres AVL ?
La plupart des opérations BST (par exemple, recherche, max, min, insertion, suppression, etc.) prennent Oh) moment où h est la hauteur du BST. Le coût de ces opérations peut devenir Sur) pour un arbre binaire asymétrique . Si l'on s'assure que la hauteur de l'arbre reste O(log(n)) après chaque insertion et suppression, nous pouvons alors garantir une limite supérieure de O(log(n)) pour toutes ces opérations. La hauteur d'un arbre AVL est toujours O(log(n)) où n est le nombre de nœuds dans l'arborescence.
Insertion dans l'arborescence AVL :
Pour nous assurer que l'arborescence donnée reste AVL après chaque insertion, nous devons augmenter l'opération d'insertion BST standard pour effectuer un rééquilibrage.
Voici deux opérations de base qui peuvent être effectuées pour équilibrer un BST sans violer la propriété BST (touches (à gauche)
- Rotation à gauche
- Rotation à droite
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 et /<- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Pratique recommandée Insertion d'arbre AVL Essayez-le !
Étapes à suivre pour l'insertion :
Laissez le nœud nouvellement inséré être Dans
- Effectuer la norme BST insérer pour Dans .
- A partir de Dans , voyagez et trouvez le premier nœud déséquilibré . Laisser Avec être le premier nœud déséquilibré, et Soit le enfant de Avec qui vient sur le chemin de Dans à Avec et X Soit le petit enfant de Avec qui vient sur le chemin de Dans à Avec .
- Rééquilibrez l'arbre en effectuant des rotations appropriées sur le sous-arbre dont la racine est Avec. Il peut y avoir 4 cas possibles qui doivent être traités comme x,y et Avec peut être disposé de 4 manières.
- Voici les 4 arrangements possibles :
- y est l'enfant gauche de z et x est l'enfant gauche de y (Left Left Case)
- y est l'enfant gauche de z et x est l'enfant droit de y (Cas Gauche Droit)
- y est le bon enfant de z et x est le bon enfant de y (Right Right Case)
- y est l'enfant droit de z et x est l'enfant gauche de y (cas droit gauche)
Voici les opérations à effectuer dans les 4 cas mentionnés ci-dessus. Dans tous les cas, il suffit de rééquilibrer le sous-arbre dont la racine est Avec et l'arbre complet s'équilibre avec la hauteur du sous-arbre (après des rotations appropriées) enraciné avec Avec devient le même qu’avant l’insertion.
1. Boîtier gauche gauche
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->//x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Boîtier gauche droit
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Bon cas
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Boîtier droit gauche
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Illustration de l'insertion dans l'arborescence AVL





Approche:
L'idée est d'utiliser l'insertion récursive BST, après insertion, nous obtenons des pointeurs vers tous les ancêtres un par un de manière ascendante. Nous n’avons donc pas besoin d’un pointeur parent pour voyager. Le code récursif lui-même remonte et visite tous les ancêtres du nœud nouvellement inséré.
Suivez les étapes mentionnées ci-dessous pour mettre en œuvre l'idée :
- Effectuer la normale Insertion de BST.
- Le nœud actuel doit être l'un des ancêtres du nœud nouvellement inséré. Mettre à jour le hauteur du nœud actuel.
- Obtenez le facteur d'équilibre (hauteur du sous-arbre gauche – hauteur du sous-arbre droit) du nœud actuel.
- Si le facteur d'équilibre est supérieur à 1, alors le nœud courant est déséquilibré et on est soit dans le Gauche Cas gauche ou gauche Boîtier droit . Pour vérifier si c'est le cas gauche boîtier gauche ou non, comparez la clé nouvellement insérée avec la clé dans le racine du sous-arbre gauche .
- Si le facteur d'équilibre est inférieur à -1 , alors le nœud actuel est déséquilibré et nous sommes soit dans le cas Droite Droite, soit dans le cas Droite-Gauche. Pour vérifier si c'est le cas Right Right ou non, comparez la clé nouvellement insérée avec la clé dans la racine du sous-arbre droit.
Vous trouverez ci-dessous la mise en œuvre de l’approche ci-dessus :
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->hauteur;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b) ? un B;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->clé = clé ;> >node->gauche = NULL ;> >node->droite = NULL ;> >node->hauteur = 1 ;>// new node is initially> >// added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->gauche;> >Node *T2 = x->droite;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->droite = y ;> >y->gauche = T2 ;> > >// Update heights> >y->hauteur = max(hauteur(y->gauche),> >height(y->à droite)) + 1 ;> >x->hauteur = max(hauteur(x->gauche),> >height(x->à droite)) + 1 ;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->droite;> >Node *T2 = y->gauche;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->gauche = x ;> >x->à droite = T2 ;> > >// Update heights> >x->hauteur = max(hauteur(x->gauche),> >height(x->à droite)) + 1 ;> >y->hauteur = max(hauteur(y->gauche),> >height(y->à droite)) + 1 ;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->gauche) - hauteur(N->droite);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(nœud->gauche, clé);> >else> if> (key>nœud->clé)> >node->right = insert (nœud->right, clé);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->hauteur = 1 + max(hauteur(nœud->gauche),> >height(node->droite));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && touche gauche->touche)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->droite->touche)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 touche &&> nœud->gauche->touche)> >{> >node->left = leftRotate(node->left);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->touche)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(noeud->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->gauche); preOrder(root->right); } } // Code du pilote int main() { Nœud *root = NULL ; /* Construction de l'arbre donné dans la figure ci-dessus */ root = insert(root, 10); racine = insert(racine, 20); racine = insert(racine, 30); racine = insert(racine, 40); racine = insert(racine, 50); racine = insert(racine, 25); /* L'arbre AVL construit serait 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->hauteur;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b) ? un B;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->clé = clé ;> >node->gauche = NULL ;> >node->droite = NULL ;> >node->hauteur = 1 ;>// new node is initially added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->gauche;> >struct> Node *T2 = x->droite;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->droite = y ;> >y->gauche = T2 ;> > >// Update heights> >y->hauteur = max(hauteur(y->gauche),> >height(y->à droite)) + 1 ;> >x->hauteur = max(hauteur(x->gauche),> >height(x->à droite)) + 1 ;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->droite;> >struct> Node *T2 = y->gauche;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->gauche = x ;> >x->à droite = T2 ;> > >// Update heights> >x->hauteur = max(hauteur(x->gauche),> >height(x->à droite)) + 1 ;> >y->hauteur = max(hauteur(y->gauche),> >height(y->à droite)) + 1 ;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->gauche) - hauteur(N->droite);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert (nœud->gauche, clé);> >else> if> (key>nœud->clé)> >node->right = insert (nœud->right, clé);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->hauteur = 1 + max(hauteur(nœud->gauche),> >height(node->droite));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && touche gauche->touche)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->droite->touche)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 touche &&> nœud->gauche->touche)> >{> >node->left = leftRotate(node->left);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->touche)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(noeud->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->clé);> >preOrder(root->gauche);> >preOrder(root->droite);> >}> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>b) ? un B;> >}> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, clé); else // Les clés en double ne sont pas autorisées return node; /* 2. Mettre à jour la hauteur de ce nœud ancêtre */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Obtenez le facteur d'équilibre de ce nœud ancêtre pour vérifier si ce nœud est devenu déséquilibré */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Si ce nœud devient déséquilibré, alors il y a // 4 cas Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance<-1 && key>node.right.key) return leftRotate(node); // Cas gauche droite if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate (nœud); } // Droite Gauche Cas if (solde<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 et la clé renvoient self.rightRotate(root) # Cas 2 - Droite Droite si équilibre<-1 and key>root.right.val : return self.leftRotate(root) # Cas 3 - Gauche Droite si balance> 1 et clé> root.left.val : root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root ) # Cas 4 - Droite Gauche si équilibre<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>b) ? un B;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, clé); else // Les clés en double ne sont pas autorisées return node; /* 2. Mettre à jour la hauteur de ce nœud ancêtre */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Obtenez le facteur d'équilibre de ce nœud ancêtre pour vérifier si ce nœud est devenu déséquilibré */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Si ce nœud devient déséquilibré, alors il // y a 4 cas Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // Cas gauche droit if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); // Cas droit gauche if (balance);<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b ? un B;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = this.insert(node.right, key); // Les clés en double ne sont pas autorisées, sinon return node ; /* 2. Mettre à jour la hauteur de ce nœud ancêtre */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(node.left), this.height(node.right)); /* 3. Obtenez le facteur d'équilibre de ce nœud ancêtre pour vérifier si ce nœud est devenu déséquilibré */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Si ce nœud devient déséquilibré, alors il y a // 4 cas Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) renvoie this. leftRotate(node); // Gauche Droite Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left); return this.rightRotate(node); Cas gauche si (solde<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root);> |
>
>Sortir
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Analyse de complexité
Complexité temporelle : O (log (n)), pour insertion
Espace auxiliaire : O(1)
pointeur de déréférencement c
Les opérations de rotation (rotation à gauche et à droite) prennent un temps constant car seuls quelques pointeurs y sont modifiés. La mise à jour de la hauteur et l'obtention du facteur d'équilibre prennent également un temps constant. Ainsi, la complexité temporelle de l'insert AVL reste la même que celle de l'insert BST qui est O(h) où h est la hauteur de l'arbre. Puisque l’arborescence AVL est équilibrée, la hauteur est O(Logn). La complexité temporelle de l'insertion AVL est donc O (Logn).
Comparaison avec l'arbre rouge noir :
L'arborescence AVL et d'autres arbres de recherche auto-équilibrés comme Red Black sont utiles pour effectuer toutes les opérations de base en un temps O (log n). Les arbres AVL sont plus équilibrés que les arbres rouge-noir, mais ils peuvent provoquer davantage de rotations lors de l'insertion et de la suppression. Ainsi, si votre application implique de nombreuses insertions et suppressions fréquentes, les arbres Rouge Noir doivent être préférés. Et si les insertions et les suppressions sont moins fréquentes et que la recherche est l'opération la plus fréquente, alors l'arborescence AVL doit être préférée à Red Black Tree .
Voici le message à supprimer dans l'arborescence AVL :
Arbre AVL | Ensemble 2 (suppression)
