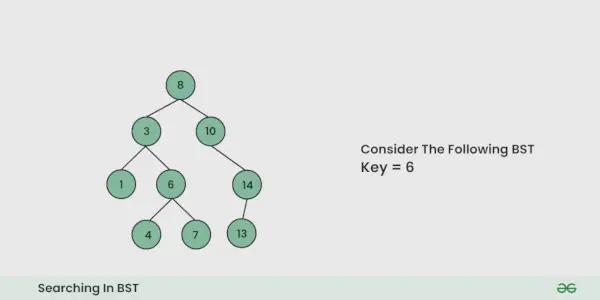
Donné un BST , la tâche consiste à rechercher un nœud dans ce BST .
Pour rechercher une valeur dans BST, considérez-la comme un tableau trié. Nous pouvons maintenant facilement effectuer une opération de recherche dans BST en utilisant Algorithme de recherche binaire .
Algorithme pour rechercher une clé dans un arbre de recherche binaire donné :
Disons que nous voulons rechercher le numéro X, Nous commençons par la racine. Alors:
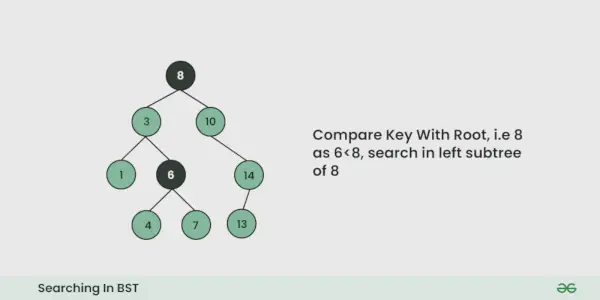
- On compare la valeur à rechercher avec la valeur de la racine.
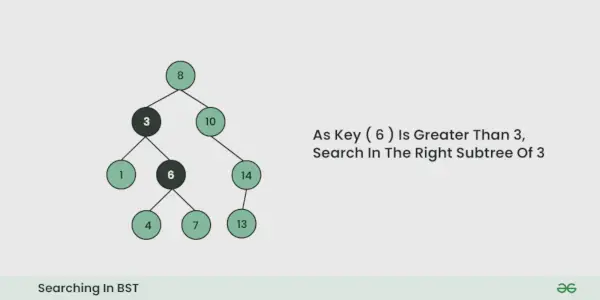
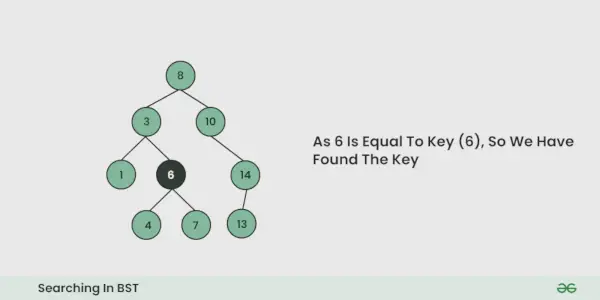
- Si c'est égal, nous avons terminé la recherche, si c'est plus petit, nous savons que nous devons aller au sous-arbre de gauche car dans un arbre de recherche binaire, tous les éléments du sous-arbre de gauche sont plus petits et tous les éléments du sous-arbre de droite sont plus grands.
- Répétez l'étape ci-dessus jusqu'à ce qu'il n'y ait plus de traversée possible
- Si à une itération, la clé est trouvée, retournez True. Sinon faux.
Illustration d'une recherche dans un BST :
Voir l'illustration ci-dessous pour une meilleure compréhension :
apurva padgaonkar
Pratique recommandéeRecherchez un nœud dans BSTTry It !
Programme pour implémenter la recherche dans BST :
C++
// C++ function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> using> namespace> std;> struct> node {> >int> key;> >struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(>int> item)> {> >struct> node* temp> >=>new> struct> node;> >temp->clé = élément ;> >temp->gauche = temp->droite = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(>struct> node* node,>int> key)> {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node == NULL)> >return> newNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(node->left, key);> >else> if> (key>nœud->clé)> >node->right = insert(node->right, key);> >// Return the (unchanged) node pointer> >return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(>struct> node* root,>int> key)> > >// Base Cases: root is null or key is present at root> >if> (root == NULL> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >struct> node* root = NULL;> >root = insert(root, 50);> >insert(root, 30);> >insert(root, 20);> >insert(root, 40);> >insert(root, 70);> >insert(root, 60);> >insert(root, 80);> >// Key to be found> >int> key = 6;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >cout << key <<>' not found'> << endl;> >else> >cout << key <<>' found'> << endl;> >key = 60;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >cout << key <<>' not found'> << endl;> >else> >cout << key <<>' found'> << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
C
centos contre rhel
// C function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> #include> struct> node {> >int> key;> >struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(>int> item)> {> >struct> node* temp> >= (>struct> node*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node));> >temp->clé = élément ;> >temp->gauche = temp->droite = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(>struct> node* node,>int> key)> {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node == NULL)> >return> newNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(node->left, key);> >else> if> (key>nœud->clé)> >node->right = insert(node->right, key);> >// Return the (unchanged) node pointer> >return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(>struct> node* root,>int> key)> > // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >struct> node* root = NULL;> >root = insert(root, 50);> >insert(root, 30);> >insert(root, 20);> >insert(root, 40);> >insert(root, 70);> >insert(root, 60);> >insert(root, 80);> >// Key to be found> >int> key = 6;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >printf>(>'%d not found
'>, key);> >else> >printf>(>'%d found
'>, key);> >key = 60;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >printf>(>'%d not found
'>, key);> >else> >printf>(>'%d found
'>, key);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node {> >int> key;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item) {> >key = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> BinarySearchTree {> >Node root;> >// Constructor> >BinarySearchTree() {> >root =>null>;> >}> >// A utility function to insert> >// a new node with given key in BST> >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node ==>null>) {> >node =>new> Node(key);> >return> node;> >}> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, clé); // Renvoie le pointeur de nœud (inchangé) return node; } // Fonction utilitaire pour rechercher une clé dans une recherche de nœud BST (racine du nœud, clé int) // Code du pilote public static void main (String [] args) { BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree (); // Insertion de nœuds tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 30); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 20); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 40); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 70); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 60); arbre.insert(arbre.racine, 80); // Clé à trouver int key = 6; // Recherche dans un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' not found'); else System.out.println(key + 'found'); clé = 60 ; // Recherche dans un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' not found'); else System.out.println(key + 'found'); } }> |
>
>
Python3
algorithme de tri par insertion
# Python3 function to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # A utility function to insert> # a new node with the given key in BST> def> insert(node, key):> ># If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> node>is> None>:> >return> Node(key)> ># Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> key node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key>node.key: node.right = insert(node.right, key) # Renvoie le nœud de retour du pointeur de nœud (inchangé) # Fonction utilitaire pour rechercher une clé dans une recherche de définition BST (root, key) : # Cas de base : root is null ou la clé est présente à la racine si root est None ou root.key == key: return root # La clé est supérieure à la clé de root si root.key return search(root.right, key) # La clé est plus petite que la racine La clé de renvoie la recherche (root.left, key) # Code du pilote si __name__ == '__main__' : root = Aucun root = insert (root, 50) insert (root, 30) insert (root, 20) insert (root, 40) insert(root, 70) insert(root, 60) insert(root, 80) # Clé à trouver key = 6 # Recherche dans un BST si search(root, key) est Aucun : print(key, 'not found') else : print(key, 'found') key = 60 # Recherche dans un BST si search(root, key) est None : print(key, 'not found') else : print(clé, 'trouvé')> |
>
>
C#
conversion de date en chaîne
// C# function to search a given key in a given BST> using> System;> public> class> Node {> >public> int> key;> >public> Node left, right;> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// A utility function to create a new BST node> >public> Node NewNode(>int> item)> >{> >Node temp =>new> Node();> >temp.key = item;> >temp.left = temp.right =>null>;> >return> temp;> >}> >// A utility function to insert> >// a new node with given key in BST> >public> Node Insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> NewNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key node.left = Insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = Insérer (node.right, clé); // Renvoie le pointeur de nœud (inchangé) return node; } // Fonction utilitaire pour rechercher une clé dans une recherche de nœud public BST (racine du nœud, clé int) // Cas de base : la racine est nulle ou la clé est présente à la racine si (root == null // Code du pilote public static void Main () { Noeud racine = null BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); racine = bt.Insert(racine, 50); , 40); bt.Insert(root, 70); bt.Insert(root, 60); bt.Insert(root, 80); // Clé à trouver int key = 6; bt.Search(root, key) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' not found'); else Console.WriteLine(key + ' found'); // Recherche dans un BST; if (bt.Search(root, key) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' not found'); else Console.WriteLine (key + ' found' } }>'>); |
>RJ12 contre RJ11
// Javascript function to search a given key in a given BST>class Node {>>constructor(key) {>>this>.key = key;>>this>.left =>null>;>>this>.right =>null>;>>}>}>// A utility function to insert>// a new node with given key in BST>function>insert(node, key) {>>// If the tree is empty, return a new node>>if>(node ===>null>) {>>return>new>Node(key);>>}>>// Otherwise, recur down the tree>>if>(key node.left = insert(node.left, key); } else if (key>node.key) { node.right = insert(node.right, clé); } // Renvoie le pointeur de nœud (inchangé) return node; } // Fonction utilitaire pour rechercher une clé dans une fonction BST search(root, key) { // Cas de base : la racine est nulle ou la clé est présente à la racine if (root === null || root.key === key ) { retourner la racine ; } // La clé est supérieure à la clé de root if (root.key return search(root.right, key); } // La clé est plus petite que la clé de root return search(root.left, key); } // Code du pilote let root = null; insert(root, 50); insert(root, 20); 60); insert(root, 80); // Clé à trouver let key = 6; // Recherche dans un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log(key + ' not found'); } else { console.log(key + ' found'); } key = 60; // Recherche dans un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log( clé + 'introuvable'); } else { console.log(clé + 'trouvé' }>'>);>6 not found 60 found> Complexité temporelle : O(h), où h est la hauteur du BST.
Espace auxiliaire : O(h), où h est la hauteur du BST. En effet, la quantité maximale d'espace nécessaire pour stocker la pile de récursion serait h .Liens connexes:
- Opération d'insertion d'arbre de recherche binaire
- Opération de suppression de l'arbre de recherche binaire