Un tableau 2D peut être défini comme un tableau de tableaux. Le tableau 2D est organisé sous forme de matrices qui peuvent être représentées comme un ensemble de lignes et de colonnes.
Cependant, des tableaux 2D sont créés pour implémenter une structure de données similaire à une base de données relationnelle. Il permet de conserver facilement une grande quantité de données à la fois, qui peuvent être transmises à n'importe quel nombre de fonctions lorsque cela est nécessaire.
Comment déclarer un tableau 2D
La syntaxe de déclaration d'un tableau à deux dimensions est très similaire à celle d'un tableau à une dimension, donnée comme suit.
monliviricket
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
cependant, il produit la structure de données qui ressemble à la suivante.
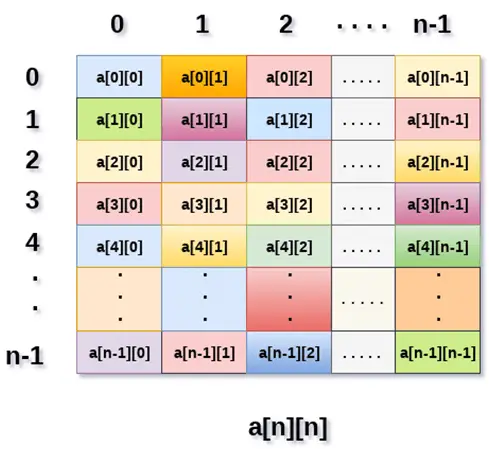
L'image ci-dessus montre le tableau bidimensionnel, les éléments sont organisés sous forme de lignes et de colonnes. Le premier élément de la première ligne est représenté par a[0][0] où le nombre affiché dans le premier index est le numéro de cette ligne tandis que le nombre affiché dans le deuxième index est le numéro de la colonne.
Comment accéder aux données dans un tableau 2D
En raison du fait que les éléments des tableaux 2D sont accessibles de manière aléatoire. Semblable aux tableaux unidimensionnels, nous pouvons accéder aux cellules individuelles d'un tableau 2D en utilisant les indices des cellules. Il y a deux indices attachés à une cellule particulière, l'un est son numéro de ligne tandis que l'autre est son numéro de colonne.
Cependant, nous pouvons stocker la valeur stockée dans n'importe quelle cellule particulière d'un tableau 2D dans une variable x en utilisant la syntaxe suivante.
image de démarque
int x = a[i][j];
où i et j sont respectivement le numéro de ligne et de colonne de la cellule.
Nous pouvons attribuer à chaque cellule d'un tableau 2D la valeur 0 en utilisant le code suivant :
for ( int i=0; i<n ;i++) { for (int j="0;" j<n; j++) a[i][j]="0;" } < pre> <h2>Initializing 2D Arrays </h2> <p>We know that, when we declare and initialize one dimensional array in C programming simultaneously, we don't need to specify the size of the array. However this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. </p> <p>The syntax to declare and initialize the 2D array is given as follows. </p> <pre> int arr[2][2] = {0,1,2,3}; </pre> <p>The number of elements that can be present in a 2D array will always be equal to ( <strong>number of rows * number of columns</strong> ). </p> <p> <strong>Example :</strong> Storing User's data into a 2D array and printing it. </p> <p> <strong>C Example : </strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf('enter a[%d][%d]: ',i,j); scanf('%d',&arr[i][j]); } printf('
printing the elements ....
'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf('
'); printf('%d ',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print('enter element'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println('printing elements...'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+' '); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline('enter element'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline('printing elements...'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+' '); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></n> Le nombre d'éléments pouvant être présents dans un tableau 2D sera toujours égal à ( nombre de lignes * nombre de colonnes ).
supprimer le fichier en java
Exemple : Stocker les données de l'utilisateur dans un tableau 2D et les imprimer.
Exemple C :
#include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf(\'enter a[%d][%d]: \',i,j); scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i][j]); } printf(\'
printing the elements ....
\'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf(\'
\'); printf(\'%d \',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print(\'enter element\'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println(\'printing elements...\'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+\' \'); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline(\'enter element\'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline(\'printing elements...\'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+\' \'); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)> où, B. A. est l'adresse de base ou l'adresse du premier élément du tableau a[0][0] .
tri au seau
Exemple :
a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer
Par ordre majeur de colonne
Si le tableau est déclaré par a[m][n] où m est le nombre de lignes tandis que n est le nombre de colonnes, alors l'adresse d'un élément a[i][j] du tableau stocké dans l'ordre majeur des lignes est calculée comme ,
Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA
où BA est l'adresse de base du tableau.
Exemple:
A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes
