La prise de décision est l’aspect le plus important de presque tous les langages de programmation. Comme son nom l'indique, la prise de décision nous permet d'exécuter un bloc de code particulier pour une décision particulière. Ici, les décisions sont prises sur la validité des conditions particulières. La vérification de l’état est l’épine dorsale de la prise de décision.
qu'est-ce que const en java
En Python, la prise de décision est effectuée par les instructions suivantes.
| Déclaration | Description |
|---|---|
| Si l'instruction | L'instruction if est utilisée pour tester une condition spécifique. Si la condition est vraie, un bloc de code (if-block) sera exécuté. |
| Si - sinon Déclaration | L'instruction if-else est similaire à l'instruction if, sauf qu'elle fournit également le bloc de code pour le cas faux de la condition à vérifier. Si la condition fournie dans l'instruction if est fausse, alors l'instruction else sera exécutée. |
| Instruction if imbriquée | Les instructions if imbriquées nous permettent d'utiliser if ? instruction else à l'intérieur d'une instruction if externe. |
Indentation en Python
Pour faciliter la programmation et par souci de simplicité, python n'autorise pas l'utilisation de parenthèses pour le code au niveau du bloc. En Python, l'indentation est utilisée pour déclarer un bloc. Si deux instructions sont au même niveau d’indentation, elles font alors partie du même bloc.
Généralement, quatre espaces sont donnés pour indenter les instructions qui représentent une quantité d'indentation typique en python.
L'indentation est la partie la plus utilisée du langage python puisqu'elle déclare le bloc de code. Toutes les instructions d'un bloc sont destinées au même niveau d'indentation. Nous verrons comment l'indentation réelle se produit dans la prise de décision et d'autres éléments en python.
L'instruction if
L'instruction if est utilisée pour tester une condition particulière et si la condition est vraie, elle exécute un bloc de code appelé if-block. La condition de l'instruction if peut être n'importe quelle expression logique valide qui peut être évaluée comme vraie ou fausse.
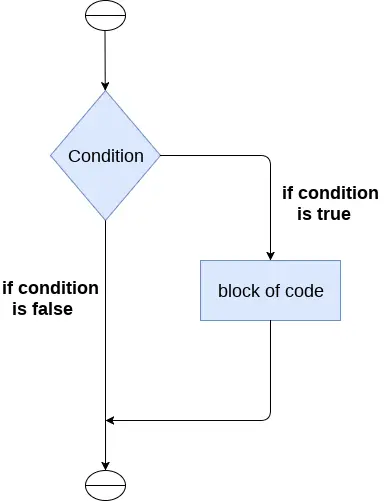
La syntaxe de l'instruction if est donnée ci-dessous.
nginx
if expression: statement
Exemple 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Sortir:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Exemple 2 : Programme pour imprimer le plus grand des trois nombres.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Sortir:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
L'instruction if-else
L'instruction if-else fournit un bloc else combiné avec l'instruction if qui est exécutée dans le cas faux de la condition.
Si la condition est vraie, alors le bloc if est exécuté. Sinon, le bloc else est exécuté.

La syntaxe de l'instruction if-else est donnée ci-dessous.
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Exemple 1 : Programme permettant de vérifier si une personne a le droit de voter ou non.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Sortir:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Exemple 2 : Programme pour vérifier si un nombre est pair ou non.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Sortir:
rendre le script exécutable
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
La déclaration elif
L'instruction elif nous permet de vérifier plusieurs conditions et d'exécuter le bloc d'instructions spécifique en fonction de la vraie condition parmi elles. Nous pouvons avoir n'importe quel nombre d'instructions elif dans notre programme en fonction de nos besoins. Cependant, l'utilisation d'elif est facultative.
L'instruction elif fonctionne comme une instruction à relais if-else-if en C. Elle doit être remplacée par une instruction if.
La syntaxe de l'instruction elif est donnée ci-dessous.
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Exemple 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Sortir:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Exemple 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 