Tri par fusion est un algorithme de tri qui suit le diviser et conquérir approche. Il fonctionne en divisant de manière récursive le tableau d'entrée en sous-tableaux plus petits et en triant ces sous-tableaux, puis en les fusionnant à nouveau pour obtenir le tableau trié.
En termes simples, nous pouvons dire que le processus de tri par fusion consiste à diviser le tableau en deux moitiés, à trier chaque moitié, puis à fusionner les moitiés triées ensemble. Ce processus est répété jusqu'à ce que l'ensemble du tableau soit trié.
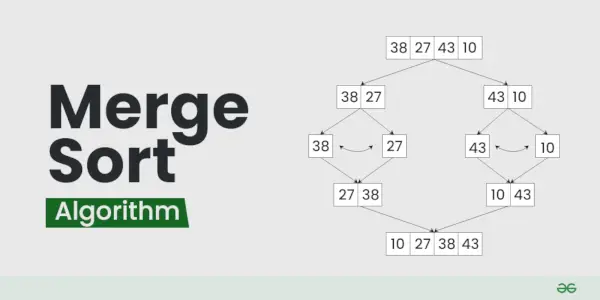
Algorithme de tri par fusion
exemple de nom d'utilisateur
Comment fonctionne le tri par fusion ?
Le tri par fusion est un algorithme de tri populaire connu pour son efficacité et sa stabilité. Il suit le diviser et conquérir approche pour trier un tableau donné d’éléments.
Voici une explication étape par étape du fonctionnement du tri par fusion :
- Diviser: Divisez la liste ou le tableau de manière récursive en deux moitiés jusqu'à ce qu'il ne puisse plus être divisé.
- Conquérir: Chaque sous-tableau est trié individuellement à l'aide de l'algorithme de tri par fusion.
- Fusionner: Les sous-tableaux triés sont fusionnés dans un ordre trié. Le processus se poursuit jusqu'à ce que tous les éléments des deux sous-tableaux aient été fusionnés.
Illustration du tri par fusion :
Trions le tableau ou la liste [38, 27, 43, 10] en utilisant le tri par fusion
Pratique recommandée Essayez-le !Regardons le fonctionnement de l'exemple ci-dessus :
Diviser:
modules à ressorts
- [38, 27, 43, 10] est divisé en [38, 27 ] et [43, 10] .
- [38, 27] est divisé en [38] et [27] .
- [43, 10] est divisé en [43] et [dix] .
Conquérir:
noeud de liste Java
- [38] est déjà trié.
- [27] est déjà trié.
- [43] est déjà trié.
- [dix] est déjà trié.
Fusionner:
- Fusionner [38] et [27] obtenir [27, 38] .
- Fusionner [43] et [dix] obtenir [10.43] .
- Fusionner [27, 38] et [10.43] pour obtenir la liste triée finale [10, 27, 38, 43]
La liste triée est donc [10, 27, 38, 43] .
Implémentation du tri par fusion :
C++ // C++ program for Merge Sort #include using namespace std; // Merges two subarrays of array[]. // First subarray is arr[begin..mid] // Second subarray is arr[mid+1..end] void merge(int array[], int const left, int const mid, int const right) { int const subArrayOne = mid - left + 1; int const subArrayTwo = right - mid; // Create temp arrays auto *leftArray = new int[subArrayOne], *rightArray = new int[subArrayTwo]; // Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for (auto i = 0; i < subArrayOne; i++) leftArray[i] = array[left + i]; for (auto j = 0; j < subArrayTwo; j++) rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j]; auto indexOfSubArrayOne = 0, indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0; int indexOfMergedArray = left; // Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne && indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { if (leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; } else { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; } indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // left[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // right[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; indexOfMergedArray++; } delete[] leftArray; delete[] rightArray; } // begin is for left index and end is right index // of the sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int array[], int const begin, int const end) { if (begin>= fin) retour ; int mid = début + (fin - début) / 2 ; mergeSort (tableau, début, milieu); mergeSort(tableau, milieu + 1, fin); fusionner (tableau, début, milieu, fin); } // FONCTIONS UTILITAIRES // Fonction pour imprimer un tableau void printArray(int A[], int size) { for (int i = 0; i< size; i++) cout << A[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); cout << 'Given array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); cout << '
Sorted array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; } // This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi // This code was revised by Joshua Estes> C // C program for Merge Sort #include #include // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { int i, j, k; int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[n1], R[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r i = 0; j = 0; k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves mergeSort(arr, l, m); mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r); merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // Function to print an array void printArray(int A[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) printf('%d ', A[i]); printf('
'); } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); printf('Given array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); printf('
Sorted array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; }> Java // Java program for Merge Sort import java.io.*; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[] = new int[n1]; int R[] = new int[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indices of first and second subarrays int i = 0, j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to print array of size n static void printArray(int arr[]) { int n = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) System.out.print(arr[i] + ' '); System.out.println(); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; System.out.println('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); System.out.println('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */> Python # Merges two subarrays of array[]. # First subarray is arr[left..mid] # Second subarray is arr[mid+1..right] def merge(array, left, mid, right): subArrayOne = mid - left + 1 subArrayTwo = right - mid # Create temp arrays leftArray = [0] * subArrayOne rightArray = [0] * subArrayTwo # Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for i in range(subArrayOne): leftArray[i] = array[left + i] for j in range(subArrayTwo): rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j] indexOfSubArrayOne = 0 # Initial index of first sub-array indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0 # Initial index of second sub-array indexOfMergedArray = left # Initial index of merged array # Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne and indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: if leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 else: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of left[], if any while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of right[], if any while indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # begin is for left index and end is right index # of the sub-array of arr to be sorted def mergeSort(array, begin, end): if begin>= end: return mid = start + (end - start) // 2 mergeSort(array, start, mid) mergeSort(array, mid + 1, end) merge(array, start, mid, end) # Fonction pour imprimer un tableau def printArray(array, size): pour i dans range(size): print(array[i], end=' ') print() # Code du pilote si __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [12 , 11, 13, 5, 6, 7] arr_size = len(arr) print('Le tableau donné est') printArray(arr, arr_size) mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1) print('
Tableau trié est') printArray(arr, arr_size)> C# // C# program for Merge Sort using System; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of []arr. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int[] arr, int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two // subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int[] L = new int[n1]; int[] R = new int[n2]; int i, j; // Copy data to temp arrays for (i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indexes of first // and second subarrays i = 0; j = 0; // Initial index of merged // subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that // sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int[] arr, int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to // print array of size n static void printArray(int[] arr) { int n = arr.Length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Console.Write(arr[i] + ' '); Console.WriteLine(); } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; Console.WriteLine('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1); Console.WriteLine('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } // This code is contributed by Princi Singh> Javascript // JavaScript program for Merge Sort // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(arr, l, m, r) { var n1 = m - l + 1; var n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays var L = new Array(n1); var R = new Array(n2); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (var i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (var j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] // Initial index of first subarray var i = 0; // Initial index of second subarray var j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray var k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // L[], if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // R[], if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is // right index of the sub-array // of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(arr,l, r){ if(l>=r){retour ; } var m =l+ parseInt((r-l)/2); mergeSort(arr,l,m); mergeSort(arr,m+1,r); fusionner(arr,l,m,r); } // Fonction pour imprimer un tableau function printArray( A, size) { for (var i = 0; i< size; i++) console.log( A[i] + ' '); } var arr = [ 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 ]; var arr_size = arr.length; console.log( 'Given array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); console.log( 'Sorted array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); // This code is contributed by SoumikMondal> PHP /* PHP recursive program for Merge Sort */ // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(&$arr, $l, $m, $r) { $n1 = $m - $l + 1; $n2 = $r - $m; // Create temp arrays $L = array(); $R = array(); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for ($i = 0; $i < $n1; $i++) $L[$i] = $arr[$l + $i]; for ($j = 0; $j < $n2; $j++) $R[$j] = $arr[$m + 1 + $j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] $i = 0; $j = 0; $k = $l; while ($i < $n1 && $j < $n2) { if ($L[$i] <= $R[$j]) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; } else { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; } $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while ($i < $n1) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while ($j < $n2) { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; $k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(&$arr, $l, $r) { if ($l < $r) { $m = $l + (int)(($r - $l) / 2); // Sort first and second halves mergeSort($arr, $l, $m); mergeSort($arr, $m + 1, $r); merge($arr, $l, $m, $r); } } // Function to print an array function printArray($A, $size) { for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++) echo $A[$i].' '; echo '
'; } // Driver code $arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7); $arr_size = sizeof($arr); echo 'Given array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); mergeSort($arr, 0, $arr_size - 1); echo '
Sorted array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); return 0; //This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli ?>> Sortir
Given array is 12 11 13 5 6 7 Sorted array is 5 6 7 11 12 13>
Analyse de complexité du tri par fusion :
Complexité temporelle :
- Meilleur cas: O(n log n), Lorsque le tableau est déjà trié ou presque trié.
- Cas moyen : O(n log n), Lorsque le tableau est ordonné de manière aléatoire.
- Pire cas: O(n log n), Lorsque le tableau est trié dans l'ordre inverse.
Complexité spatiale : O(n), Un espace supplémentaire est requis pour le tableau temporaire utilisé lors de la fusion.
Avantages du tri par fusion :
- La stabilité : Le tri par fusion est un algorithme de tri stable, ce qui signifie qu'il maintient l'ordre relatif des éléments égaux dans le tableau d'entrée.
- Performances garanties dans le pire des cas : Le tri par fusion a une complexité temporelle dans le pire des cas de O(N logN) , ce qui signifie qu'il fonctionne bien même sur de grands ensembles de données.
- Simple à mettre en œuvre : L’approche diviser pour régner est simple.
Inconvénient du tri par fusion :
- Complexité spatiale : Le tri par fusion nécessite de la mémoire supplémentaire pour stocker les sous-tableaux fusionnés pendant le processus de tri.
- Pas en place: Le tri par fusion n'est pas un algorithme de tri sur place, ce qui signifie qu'il nécessite de la mémoire supplémentaire pour stocker les données triées. Cela peut constituer un inconvénient dans les applications où l'utilisation de la mémoire est un problème.
Applications du tri par fusion :
- Trier de grands ensembles de données
- Tri externe (lorsque l'ensemble de données est trop volumineux pour tenir en mémoire)
- Comptage d'inversions (compter le nombre d'inversions dans un tableau)
- Trouver la médiane d'un tableau
Liens rapides:
- Articles récents sur le tri par fusion
- Principales questions et problèmes d'entretien de tri
- Problèmes pratiques sur l'algorithme de tri
- Quiz sur le tri par fusion
