Introduction:
Les raccourcisseurs d'URL sont un exemple de hachage car ils mappent une URL de grande taille à une URL de petite taille.
Quelques exemples de fonctions de hachage :
- clé % nombre de compartiments
- Valeur ASCII du caractère * PrimeNumberX. Où x = 1, 2, 3….n
- Vous pouvez créer votre propre fonction de hachage, mais ce doit être une bonne fonction de hachage qui donne moins de collisions.
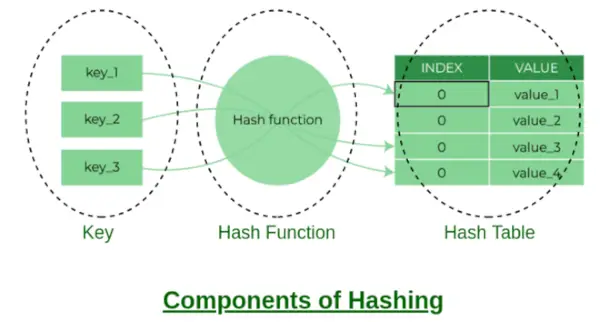
Composants du hachage
emojis pomme sur Android
Indice de compartiment :
La valeur renvoyée par la fonction Hash est l'index du bucket pour une clé dans une méthode de chaînage distincte. Chaque index du tableau est appelé un compartiment car il s'agit d'un compartiment d'une liste chaînée.
Répétition :
Le rehashing est un concept qui réduit les collisions lorsque les éléments sont augmentés dans la table de hachage actuelle. Cela créera un nouveau tableau de taille doublée et y copiera les éléments du tableau précédent. C'est comme le fonctionnement interne du vecteur en C++. Évidemment, la fonction de hachage doit être dynamique car elle doit refléter certains changements lorsque la capacité augmente. La fonction de hachage inclut la capacité de la table de hachage. Par conséquent, lors de la copie des valeurs clés de la fonction de hachage du tableau précédent, elle donne différents index de compartiment car cela dépend de la capacité (compartiments) de la table de hachage. Généralement, lorsque la valeur du facteur de charge est supérieure à 0,5, des rehachages sont effectués.
- Doublez la taille du tableau.
- Copiez les éléments du tableau précédent dans le nouveau tableau. Nous utilisons la fonction de hachage tout en copiant à nouveau chaque nœud dans un nouveau tableau. Cela réduira donc les collisions.
- Supprimez le tableau précédent de la mémoire et pointez le pointeur du tableau intérieur de votre carte de hachage vers ce nouveau tableau.
- Généralement, facteur de charge = nombre d'éléments dans Hash Map / nombre total de buckets (capacité).
Collision:
La collision est la situation dans laquelle l'index du compartiment n'est pas vide. Cela signifie qu'un en-tête de liste chaînée est présent à cet index de compartiment. Nous avons deux valeurs ou plus qui correspondent au même index de compartiment.
Principales fonctions de notre programme
- Insertion
- Recherche
- Fonction de hachage
- Supprimer
- Répéter
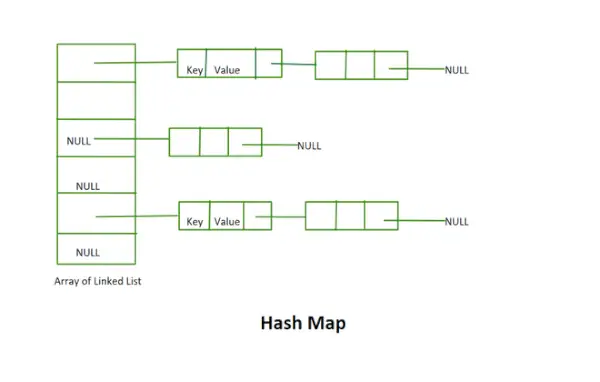
Carte de hachage
Implémentation sans ressassement :
1nf 2nf 3nf
C
#include> #include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >node->clé = clé;> >node->valeur = valeur;> >node->suivant = NULL;> >return>;> };> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp)> {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacité = 100 ;> >mp->numOfElements = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*)> >* mp->capacité);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacité)> >+ (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacité)> >% mp->capacité;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__)> >* (31 % __INT16_MAX__))> >% __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->suivant = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >return>;> }> void> delete> (>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->clé) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->suivant = currNode->suivant;> >}> >free>(currNode);> >break>;> >}> >prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->suivant;> >}> >return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting the bucket index> >// for the given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >// Head of the linked list> >// present at bucket index> >struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (bucketHead->clé == clé) {> >return> bucketHead->valeur;> >}> >bucketHead = bucketHead->suivant;> >}> >// If no key found in the hashMap> >// equal to the given key> >char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> >errorMssg =>'Oops! No data found.
'>;> >return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> >// Initialize the value of mp> >struct> hashMap* mp> >= (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> >initializeHashMap(mp);> >insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> >insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> >insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> >insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> >insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> >// Key is not inserted> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> >printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> >// Deletion of key> >delete> (mp,>'decentBoy'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >return> 0;> }> |
>
quelque chose pour les petits amis
>
C++
#include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >node->clé = clé;> >node->valeur = valeur;> >node->suivant = NULL;> >return>;> }> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp) {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacité = 100 ;> >mp->numOfElements = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*) * mp->capacité);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacité) + (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacité) % mp->capacité;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__) * (31 % __INT16_MAX__)) % __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->suivant = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> >}> >return>;> }> void> deleteKey(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->clé) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->suivant = currNode->suivant;> }> free>(currNode);> break>;> }> prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->suivant;> >}> return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> // Getting the bucket index for the given key> int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> // Head of the linked list present at bucket index> struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> > >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (>strcmp>(bucketHead->clé, clé) == 0) {> >return> bucketHead->valeur;> >}> > >bucketHead = bucketHead->suivant;> }> // If no key found in the hashMap equal to the given key> char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> strcpy>(errorMssg,>'Oops! No data found.
'>);> return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> // Initialize the value of mp> struct> hashMap* mp = (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> initializeHashMap(mp);> insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> // Key is not inserted> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> // Deletion of key> deleteKey(mp,>'decentBoy'>);> // Searching the deleted key> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> return> 0;> }> |
stlc
>
>Sortir
balançoire java
Manish Anjali Vartika Mayank techcodeview.com Oops! No data found. After deletion : Oops! No data found.>
Explication:
- insertion : insère la paire clé-valeur en tête d'une liste chaînée qui est présente à l'index de compartiment donné. hashFunction : donne l'index du bucket pour la clé donnée. Notre fonction de hachage = valeur ASCII du caractère * primeNumberX . Le nombre premier dans notre cas est 31 et la valeur de x augmente de 1 à n pour les caractères consécutifs d'une clé. suppression : supprime la paire clé-valeur de la table de hachage pour la clé donnée. Il supprime le nœud de la liste chaînée qui contient la paire clé-valeur. Rechercher : recherchez la valeur de la clé donnée.
- Cette implémentation n'utilise pas le concept de rehashing. Il s’agit d’un tableau de listes chaînées de taille fixe.
- La clé et la valeur sont toutes deux des chaînes dans l'exemple donné.
Complexité temporelle et complexité spatiale :
La complexité temporelle des opérations d’insertion et de suppression de tables de hachage est en moyenne de O(1). Il existe des calculs mathématiques qui le prouvent.
- Complexité temporelle de l'insertion : dans le cas moyen, elle est constante. Dans le pire des cas, c’est linéaire. Complexité temporelle de la recherche : dans le cas moyen, elle est constante. Dans le pire des cas, c’est linéaire. Complexité temporelle de la suppression : dans les cas moyens, elle est constante. Dans le pire des cas, c’est linéaire. Complexité spatiale : O(n) car il comporte un nombre n d'éléments.
Articles Liés:
- Technique de gestion des collisions de chaînage séparé dans le hachage.
