Le chiffre ROT13 (lu comme – rotation de 13 places) est un cas particulier du chiffre Ceaser dans lequel le décalage est toujours de 13.
Ainsi, chaque lettre est décalée de 13 places pour chiffrer ou déchiffrer le message.
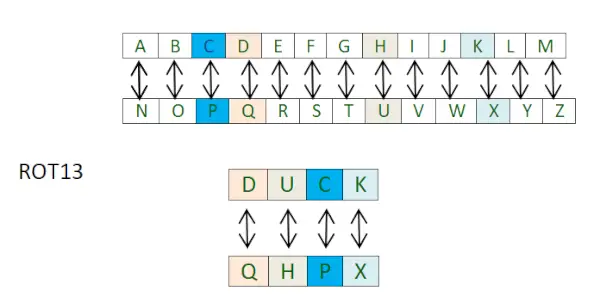
Vous devez penser que ce n'est qu'un autre chiffre de César, alors qu'est-ce qui est différent cette fois ? Eh bien, la différence réside dans sa mise en œuvre. L'approche consiste à utiliser deux dictionnaires Python distincts.
- Premier à rechercher les différentes lettres en fonction de leur place dans les alphabets anglais pour obtenir le numéro décalé
- Deuxième pour obtenir les lettres qui correspondent à ces nombres décalés.
Mise en œuvre:
C++
// CPP program to implement> // ROT13 Caesar Cipher> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Map to lookup the index of alphabets> map <>char>,>int>>dict1;> // Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> // to the index after shift> map <>int>,>char>>dict2;> // Function to create map to lookup> void> create_dict()> {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1[>char>(64 + i)] = i;> > >dict2[0] =>'Z'>;> > >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2[i] =>char>(64 + i);> > >return>;> }> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> string encrypt(string message,>int> shift)> {> >string cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i { // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i { // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code int main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; cout << encrypt(message, shift) << '
'; message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; cout << decrypt(message, shift) << '
'; return 0; } // This code is contributed by Sachin Bisht> |
>
>
Java
// java program for the above approach> import> java.util.*;> public> class> Main {> >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >static> Map dict1 =>new> HashMap();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >static> Map dict2 =>new> HashMap();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>27>; i++)> >dict1.put((>char>)(>64> + i), i);> >dict2.put(>0>,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>26>; i++)> >dict2.put(i, (>char>)(>64> + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >static> String encrypt(String message,>int> shift) {> >String cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i =>0>; i // Checking for namespace if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided static String decrypt(String message, int shift) { String decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { create_dict(); String message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; System.out.println(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; System.out.println(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // This code is contributed by prince> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to implement> # ROT13 Caesar cipher> '''This script uses dictionaries instead of 'chr()' & 'ord()' function'''> # Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> dict1>=> {>'A'> :>1>,>'B'> :>2>,>'C'> :>3>,>'D'> :>4>,>'E'> :>5>,> >'F'> :>6>,>'G'> :>7>,>'H'> :>8>,>'I'> :>9>,>'J'> :>10>,> >'K'> :>11>,>'L'> :>12>,>'M'> :>13>,>'N'> :>14>,>'O'> :>15>,> >'P'> :>16>,>'Q'> :>17>,>'R'> :>18>,>'S'> :>19>,>'T'> :>20>,> >'U'> :>21>,>'V'> :>22>,>'W'> :>23>,>'X'> :>24>,>'Y'> :>25>,>'Z'> :>26>}> # Dictionary to lookup alphabets> # corresponding to the index after shift> dict2>=> {>0> :>'Z'>,>1> :>'A'>,>2> :>'B'>,>3> :>'C'>,>4> :>'D'>,>5> :>'E'>,> >6> :>'F'>,>7> :>'G'>,>8> :>'H'>,>9> :>'I'>,>10> :>'J'>,> >11> :>'K'>,>12> :>'L'>,>13> :>'M'>,>14> :>'N'>,>15> :>'O'>,> >16> :>'P'>,>17> :>'Q'>,>18> :>'R'>,>19> :>'S'>,>20> :>'T'>,> >21> :>'U'>,>22> :>'V'>,>23> :>'W'>,>24> :>'X'>,>25> :>'Y'>}> # Function to encrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> encrypt(message, shift):> >cipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checking for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># adds the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>+> shift )>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for> ># the shifted alphabets and adds them> >cipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >cipher>+>=> ' '> >return> cipher> # Function to decrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> decrypt(message, shift):> >decipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checks for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># subtracts the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>-> shift>+> 26>)>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for the> ># shifted alphabets and adds them> >decipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >decipher>+>=> ' '> >return> decipher> # driver function to run the program> def> main():> ># use 'upper()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase> >message>=> 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> encrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> >message>=> 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> decrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> # Executes the main function> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >main()> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> using> System.Collections;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> using> System.Linq;> // C# program for the above approach> class> HelloWorld {> > >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >public> static> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>dict1 =>new> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >public> static> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>dict2 =>new> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >public> static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1.Add((>char>)(64 + i), i);> >dict2.Add(0,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2.Add(i, (>char>)(64 + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >public> static> string> encrypt(>string> message,>int> shift) {> >string> cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided public static string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]]- shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } static void Main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> |
>
>
Javascript
sous-chaîne en Java
// Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> const dict1 = {>'A'>: 1,>'B'>: 2,>'C'>: 3,>'D'>: 4,>'E'>: 5,> >'F'>: 6,>'G'>: 7,>'H'>: 8,>'I'>: 9,>'J'>: 10,> >'K'>: 11,>'L'>: 12,>'M'>: 13,>'N'>: 14,>'O'>: 15,> >'P'>: 16,>'Q'>: 17,>'R'>: 18,>'S'>: 19,>'T'>: 20,> >'U'>: 21,>'V'>: 22,>'W'>: 23,>'X'>: 24,>'Y'>: 25,>'Z'>: 26};> // Dictionary to lookup alphabets> // corresponding to the index after shift> const dict2 = {0:>'Z'>, 1:>'A'>, 2:>'B'>, 3:>'C'>, 4:>'D'>, 5:>'E'>,> >6:>'F'>, 7:>'G'>, 8:>'H'>, 9:>'I'>, 10:>'J'>,> >11:>'K'>, 12:>'L'>, 13:>'M'>, 14:>'N'>, 15:>'O'>,> >16:>'P'>, 17:>'Q'>, 18:>'R'>, 19:>'S'>, 20:>'T'>,> >21:>'U'>, 22:>'V'>, 23:>'W'>, 24:>'X'>, 25:>'Y'>};> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> function> encrypt(message, shift) {> >let cipher =>''>;> >for> (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checking for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // adds the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for // the shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided function decrypt(message, shift) { let decipher = ''; for (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checks for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // subtracts the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // driver function to run the program function main() { // use 'toUpperCase()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase let message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; let shift = 13; let result = encrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; result = decrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); } main(); // This code is contributed by adityashatmfh> |
>
>Sortir
TRRXF SBE TRRXF GEEKS FOR GEEKS>
Analyse: Le chiffre ROT13 n’est pas très sécurisé car il ne s’agit que d’un cas particulier du chiffre César. Le chiffre César peut être décrypté soit par analyse de fréquence, soit en essayant simplement les 25 clés, tandis que le chiffre ROT13 peut être décrypté en déplaçant simplement les lettres de 13 places. Il n’a donc aucune utilité pratique.
Application: ROT13 était utilisé dans le groupe de discussion net.jokes au début des années 1980.
