Nous pouvons multiplier deux matrices en Java en utilisant l'opérateur binaire * et en exécutant une autre boucle. Une matrice est également appelée tableau de tableaux. Nous pouvons additionner, soustraire et multiplier des matrices.
En cas de multiplication matricielle, un élément de ligne de la première matrice est multiplié par toutes les colonnes de la deuxième matrice.
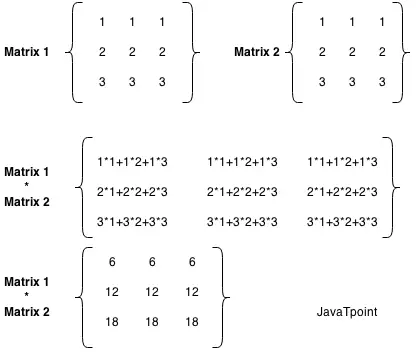
Voyons un exemple simple pour multiplier deux matrices de 3 lignes et 3 colonnes.
public class MatrixMultiplicationExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ //creating two matrices int a[][]={{1,1,1},{2,2,2},{3,3,3}}; int b[][]={{1,1,1},{2,2,2},{3,3,3}}; //creating another matrix to store the multiplication of two matrices int c[][]=new int[3][3]; //3 rows and 3 columns //multiplying and printing multiplication of 2 matrices for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j="0;j<3;j++){" c[i][j]="0;" k="0;k<3;k++)" { c[i][j]+="a[i][k]*b[k][j];" } end of loop system.out.print(c[i][j]+' '); printing matrix element system.out.println(); new line }} < pre> <span> Test it Now </span> <p>Output:</p> <pre> 6 6 6 12 12 12 18 18 18 </pre></3;i++){>