Compte tenu d'un arbre binaire la tâche est de retourner l'arbre binaire vers le bonne direction n c'est dans le sens des aiguilles d'une montre.
Saisir:
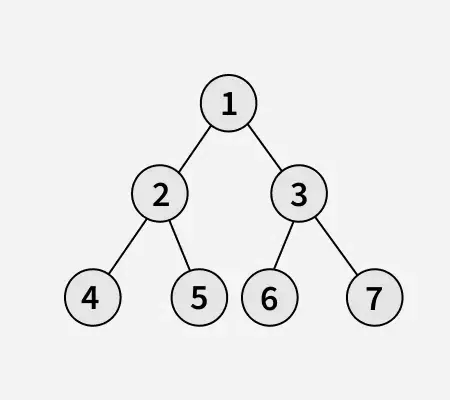
Sortir:
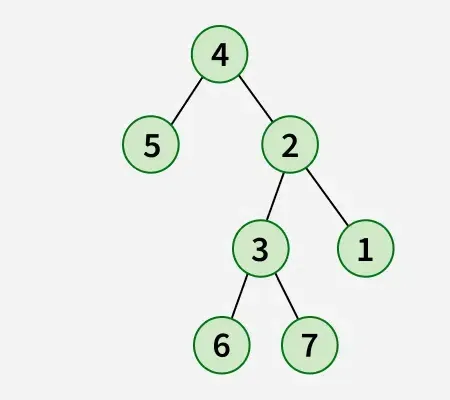
Explication: Dans l'opération de retournement, le nœud le plus à gauche devient la racine de l'arbre inversé et son parent devient son enfant droit et le frère droit devient son enfant gauche et la même chose doit être faite de manière récursive pour tous les nœuds les plus à gauche.
Table des matières
- [Approche attendue - 1] Utilisation de la récursion - O(n) Time et O(n) Space
- [Approche attendue - 2] Approche itérative - O(n) Temps et O(1) Espace
[Approche attendue - 1] Utilisation de la récursion - O(n) Time et O(n) Space
L'idée est de récursivement retournez l'arbre binaire en échangeant le gauche et droite sous-arbres de chaque nœud. Après avoir retourné la structure de l'arbre sera inversée et la nouvelle racine du arbre renversé sera le nœud feuille d'origine le plus à gauche.
Ci-dessous le principal code de rotation d'un sous-arbre :
- racine->gauche->gauche = racine->droite
- racine->gauche->droite = racine
- racine->gauche = NULL
- racine-> droite = NULL
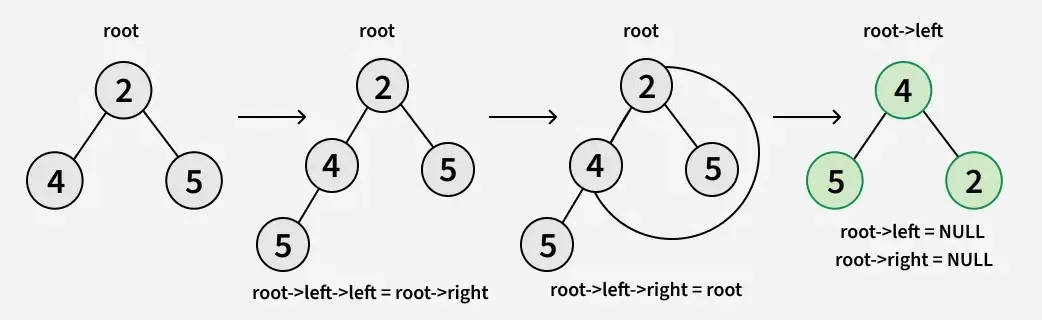
Vous trouverez ci-dessous la mise en œuvre de l’approche ci-dessus :
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree // using recursion #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Base cases if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary # tree using recursion class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def flipBinaryTree(root): # Base cases if root is None: return root if root.left is None and root.right is None: return root # Recursively call the same method flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left) # Rearranging main root Node after returning # from recursive call root.left.left = root.right root.left.right = root root.left = root.right = None return flippedRoot # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flipBinaryTree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = FlipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using recursion class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Method to flip the binary tree function flipBinaryTree(root) { if (root === null) return root; if (root.left === null && root.right === null) return root; // Recursively call the same method const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Sortir
2 3 1 4 5
[Approche attendue - 2] Approche itérative - O(n) Temps et O(n) Espace
Le solution itérative suit la même approche que le récursif la seule chose à laquelle nous devons prêter attention est économie les informations sur le nœud qui seront écrasé .
Vous trouverez ci-dessous la mise en œuvre de l’approche ci-dessus :
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree using // iterative approach #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of // prev as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize // height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary tree # using iterative approach class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Method to flip the binary tree # iteratively def flip_binary_tree(root): # Initializing the pointers to do # the swapping and storing states curr = root next = None prev = None ptr = None while curr is not None: # Pointing the next pointer to the # current next of left next = curr.left # Making the right child of prev # as curr left child curr.left = ptr # Storing the right child of # curr in ptr ptr = curr.right curr.right = prev prev = curr curr = next return prev # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flip_binary_tree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to // do the swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using iterative approach class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function flipBinaryTree(root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states let curr = root; let next = null; let prev = null; let ptr = null; while (curr !== null) { // Pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child of // curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Sortir
2 3 1 4 5



