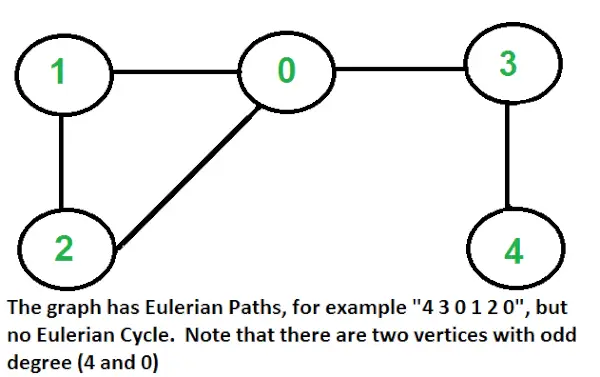
Voie eulérienne est un chemin dans un graphique qui visite chaque arête exactement une fois. Le circuit eulérien est un chemin eulérien qui commence et se termine sur le même sommet.
0,04 en fraction


Comment savoir si un graphe donné est eulérien ou non ?
Le problème est le même que la question suivante. Est-il possible de dessiner un graphique donné sans retirer le crayon du papier et sans tracer aucun des bords plus d'une fois.
Un graphe est dit eulérien s’il possède un cycle eulérien et semi-eulérien s’il possède un chemin eulérien. Le problème semble similaire au chemin hamiltonien qui est un problème NP complet pour un graphe général. Heureusement, nous pouvons déterminer si un graphe donné a ou non un chemin eulérien en temps polynomial. En fait, on peut le trouver en temps O(V+E).
Voici quelques propriétés intéressantes des graphes non orientés avec un chemin et un cycle eulériens. Nous pouvons utiliser ces propriétés pour déterminer si un graphe est eulérien ou non.
Cycle eulérien : Un graphe non orienté a un cycle eulérien si les deux conditions suivantes sont vraies.
- Tous les sommets de degré non nul sont connectés. Nous ne nous soucions pas des sommets de degré zéro car ils n'appartiennent pas au cycle ou au chemin eulérien (nous ne considérons que toutes les arêtes).
- Tous les sommets ont un degré pair.
Voie eulérienne : Un graphe non orienté a un chemin eulérien si les deux conditions suivantes sont vraies.
- Identique à la condition (a) pour le cycle eulérien.
- Si zéro ou deux sommets ont un degré impair et que tous les autres sommets ont un degré pair. Notez qu'un seul sommet de degré impair n'est pas possible dans un graphe non orienté (la somme de tous les degrés est toujours paire dans un graphe non orienté)
Notez qu’un graphe sans arêtes est considéré comme eulérien car il n’y a aucune arête à parcourir.
Comment cela marche-t-il?
Dans le chemin eulérien, chaque fois que nous visitons un sommet v, nous traversons deux arêtes non visitées avec un point final comme v. Par conséquent, tous les sommets centraux du chemin eulérien doivent avoir un degré pair. Pour le cycle eulérien, n'importe quel sommet peut être un sommet central, donc tous les sommets doivent avoir un degré pair.
Mise en œuvre:
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A class that represents an undirected graph> class> Graph> {> >int> V;>// No. of vertices> >list<>int>>*adj;>// A dynamic array of adjacency lists> public>:> >// Constructor and destructor> >Graph(>int> V) {>this>->V = V ; adj =>new> list<>int>>[DANS]; }> >~Graph() {>delete> [] adj; }>// To avoid memory leak> >// function to add an edge to graph> >void> addEdge(>int> v,>int> w);> >// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not> >int> isEulerian();> >// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >bool> isConnected();> >// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();> >void> DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[]);> };> void> Graph::addEdge(>int> v,>int> w)> {> >adj[v].push_back(w);> >adj[w].push_back(v);>// Note: the graph is undirected> }> void> Graph::DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[])> {> >// Mark the current node as visited and print it> >visited[v] =>true>;> >// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >list<>int>>::itérateur i;> >for> (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)> >if> (!visited[*i])> >DFSUtil(*i, visited);> }> // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.> // It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> bool> Graph::isConnected()> {> >// Mark all the vertices as not visited> >bool> visited[V];> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) renvoie faux ; renvoie vrai ; } /* La fonction renvoie l'une des valeurs suivantes 0 --> Si le graphe n'est pas eulérien 1 --> Si le graphe a un chemin d'Euler (semi-eulérien) 2 --> Si le graphe a un circuit d'Euler (Eulérien) */ int Graph::isEulerian() { // Vérifiez si tous les sommets de degré différent de zéro sont connectés if (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Compte les sommets de degré impair int odd = 0 ; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() & 1) odd++; // Si le nombre est supérieur à 2, alors le graphique n'est pas eulérien si (impair> 2) renvoie 0; // Si impair count est 2, alors semi-eulérien. // Si le nombre impair est 0, alors eulérien // Notez que le nombre impair ne peut jamais être 1 pour un retour de graphe non orienté (impair) } // Fonction pour exécuter des cas de test void ? test(Graphique &g) { int res = g.isEulerian(); if (res == 0) cout<< 'graph is not Eulerian
'; else if (res == 1) cout << 'graph has a Euler path
'; else cout << 'graph has a Euler cycle
'; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { // Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures Graph g1(5); g1.addEdge(1, 0); g1.addEdge(0, 2); g1.addEdge(2, 1); g1.addEdge(0, 3); g1.addEdge(3, 4); test(g1); Graph g2(5); g2.addEdge(1, 0); g2.addEdge(0, 2); g2.addEdge(2, 1); g2.addEdge(0, 3); g2.addEdge(3, 4); g2.addEdge(4, 0); test(g2); Graph g3(5); g3.addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); test(g3); // Let us create a graph with 3 vertices // connected in the form of cycle Graph g4(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); test(g4); // Let us create a graph with all vertices // with zero degree Graph g5(3); test(g5); return 0; }> |
>
>
Java
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.LinkedList;> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> LinkedList adj[];> >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> LinkedList[v];> >for> (>int> i=>0>; i adj[i] = new LinkedList(); } //Function to add an edge into the graph void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].add(w);// Add w to v's list. adj[w].add(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS void DFSUtil(int v,boolean visited[]) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { int n = i.next(); if (!visited[n]) DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from boolean isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited boolean visited[] = new boolean[V]; int i; for (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) renvoie faux ; renvoie vrai ; } /* La fonction renvoie l'une des valeurs suivantes 0 --> Si le graphe n'est pas eulérien 1 --> Si le graphe a un chemin d'Euler (semi-eulérien) 2 --> Si le graphe a un circuit d'Euler (Eulérien) */ int isEulerian() { // Vérifiez si tous les sommets de degré non nul sont connectés if (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Compte les sommets de degré impair int odd = 0 ; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size()%2!=0) odd++; // Si le nombre est supérieur à 2, alors le graphique n'est pas eulérien si (impair> 2) renvoie 0 ; / / Si le nombre impair est 2, alors semi-eulérien. // Si le nombre impair est 0, alors eulérien // Notez que le nombre impair ne peut jamais être 1 pour un retour de graphe non orienté (impair==2) ? Fonction pour exécuter des cas de test void test() { int res = isEulerian(); if (res == 0) System.out.println('graph is not Eulerian' else if (res == 1) System. out.println('graph a un chemin Euler'); else System.out.println('graph a un cycle Euler'); } // Méthode du pilote public static void main(String args[]) { / / Créons et testons les graphiques présentés dans les figures ci-dessus Graph g1 = new Graph(5); g1.addEdge(0, 2); (0, 3); g1.addEdge(3, 4); g1.test(); Graphique g2 = nouveau Graphique(5); addEdge(2, 1); g2.addEdge(0, 3); g2.addEdge(3, 4); g2.addEdge(4, 0); .addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); g3.test(); // Créons un graphe à 3 sommets // connectés sous forme de cycle Graph g4 = new Graph(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); g4.test(); // Créons un graphe avec tous les sommets // avec zéro degré Graph g5 = new Graph(3); g5.test(); } } // Ce code est contribué par Aakash Hasija> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #Complexity : O(V+E)> from> collections>import> defaultdict> # This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation> class> Graph:> >def> __init__(>self>, vertices):> >self>.V>=> vertices># No. of vertices> >self>.graph>=> defaultdict(>list>)># default dictionary to store graph> ># function to add an edge to graph> >def> addEdge(>self>, u, v):> >self>.graph[u].append(v)> >self>.graph[v].append(u)> ># A function used by isConnected> >def> DFSUtil(>self>, v, visited):> ># Mark the current node as visited> >visited[v]>=> True> ># Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >for> i>in> self>.graph[v]:> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False>:> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> >'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are> >connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> >node with non-zero degree'''> >def> isConnected(>self>):> ># Mark all the vertices as not visited> >visited>=> [>False>]>*>(>self>.V)> ># Find a vertex with non-zero degree> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i]) !>=> 0>:> >break> ># If there are no edges in the graph, return true> >if> i>=>=> self>.V>->1>:> >return> True> ># Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False> and> len>(>self>.graph[i])>>0>:> >return> False> >return> True> >'''The function returns one of the following values> >0 -->Si le graphique n'est pas eulérien> >1 -->Si le graphe a un chemin d'Euler (semi-eulérien)> >2 -->Si le graphique a un circuit d'Euler (Eulérien) '''> >def> isEulerian(>self>):> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >if> self>.isConnected()>=>=> False>:> >return> 0> >else>:> ># Count vertices with odd degree> >odd>=> 0> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i])>%> 2> !>=> 0>:> >odd>+>=> 1> >'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.> >If odd count is 0, then eulerian> >If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian> >Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''> >if> odd>=>=> 0>:> >return> 2> >elif> odd>=>=> 2>:> >return> 1> >elif> odd>>2>:> >return> 0> ># Function to run test cases> >def> test(>self>):> >res>=> self>.isEulerian()> >if> res>=>=> 0>:> >print>(>'graph is not Eulerian'>)> >elif> res>=>=> 1>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler path'>)> >else>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler cycle'>)> # Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures> g1>=> Graph(>5>)> g1.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g1.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g1.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g1.test()> g2>=> Graph(>5>)> g2.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g2.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g2.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g2.addEdge(>4>,>0>)> g2.test()> g3>=> Graph(>5>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g3.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g3.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>3>)> g3.test()> # Let us create a graph with 3 vertices> # connected in the form of cycle> g4>=> Graph(>3>)> g4.addEdge(>0>,>1>)> g4.addEdge(>1>,>2>)> g4.addEdge(>2>,>0>)> g4.test()> # Let us create a graph with all vertices> # with zero degree> g5>=> Graph(>3>)> g5.test()> # This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav> |
>
>
qu'est-ce que ça veut dire xd
C#
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> > // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> public> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> > >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> List<>int>>[]adj;> > >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> List<>int>>[dans];> >for> (>int> i=0; i adj[i] = new List |
>
>
Javascript
> // A Javascript program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class Graph> {> >// Constructor> >constructor(v)> >{> >this>.V = v;> >this>.adj =>new> Array(v);> >for> (let i = 0; i this.adj[i] = []; } // Function to add an edge into the graph addEdge(v,w) { this.adj[v].push(w);// Add w to v's list. this.adj[w].push(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS DFSUtil(v,visited) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex for(let i of this.adj[v]) { let n = i; if (!visited[n]) this.DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited let visited = new Array(this.V); let i; for (i = 0; i |
>
>Sortir
graph has a Euler path graph has a Euler cycle graph is not Eulerian graph has a Euler cycle graph has a Euler cycle>
Complexité temporelle : O(V+E)
Complexité spatiale : O(V+E)
Articles suivants :
Chemin et circuit eulérien pour des graphiques dirigés.
L'algorithme de Fleury pour imprimer un chemin ou un circuit eulérien ?
