Le commeListe() méthode de java.util.Arrays class est utilisée pour renvoyer une liste de taille fixe soutenue par le tableau spécifié. Cette méthode agit comme un pont entre les API basées sur des tableaux et basées sur des collections , en combinaison avec Collection.toArray(). La liste renvoyée est sérialisable et implémente RandomAccess.
Conseil: Cela s'exécute en temps O (1).
Syntaxe:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Paramètres: Cette méthode prend le tableau un qui doit être converti en liste. Ici… est connu sous le nom vararg qui est un tableau de paramètres et fonctionne de manière similaire à un paramètre de tableau d'objets.
vlc télécharger des vidéos youtube
Note spéciale: Le type de tableau doit être une classe Wrapper (Integer, Float, etc.) dans le cas de types de données primitifs (int, float, etc), c'est-à-dire que vous ne pouvez pas passer int a[] mais vous pouvez passer Integer a[]. Si vous transmettez int a[], cette fonction renverra un List et non List , car l'autoboxing ne se produit pas dans ce cas et int a[] est lui-même identifié comme un objet et un List of int array est renvoyé, au lieu de list d'entiers, ce qui donnera des erreurs dans diverses fonctions de collection.
Valeur de retour : Cette méthode renvoie un vue en liste du tableau spécifié.
Exemple 1:
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Sortir
tutoriel sur les microservices
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Exemple 2 :
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Sortir
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Exemple 3 :
Java
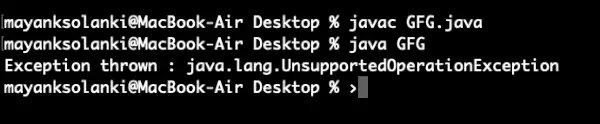
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Sortir:
caractéristiques d'une série panda