Étant donné un papier rectangulaire de dimensions un x b . La tâche consiste à découper tout le papier dans le sens minimum nombre de carré pièces. Nous pouvons choisir des morceaux carrés de n'importe quelle taille mais ils doivent être coupés sans chevauchement ni laisser d'espace supplémentaire .
Exemples :
Saisir: une = 5 b = 8
5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 5 X 8
Sortir: 5
Explication: On peut découper le papier en 5 carrés : 1 carré de taille 5x5 1 carré de taille 3x3 1 carré de taille 2x2 et 2 carrés de taille 1x1.Saisir: une = 13 b = 11
6 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 13 X 11
Sortir: 6
Explication: On peut découper le papier en 6 carrés : 1 carré de taille 7x7 1 carré de taille 6x6 1 carré de taille 5x5 2 carrés de taille 4x4 et 1 carré de taille 1x1.Saisir: une = 6 b = 7
5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 6 X 7
Sortir: 5
Explication: On peut découper le papier en 5 carrés : 1 carré de taille 4x4 2 carrés de taille 3x3 et 2 carrés de taille 3x3.
Table des matières
- [Approche incorrecte 1] Utiliser une technique gourmande
- [Approche incorrecte 2] Utilisation de la programmation dynamique
- [Approche correcte] Utilisation de DFS et de la programmation dynamique
[Approche incorrecte 1] Utiliser une technique gourmande
À première vue, il peut sembler que le problème peut être facilement résolu en découpant d'abord le plus grand carré possible dans le papier, puis en coupant le plus grand carré dans le papier restant et ainsi de suite jusqu'à ce que nous ayons coupé tout le papier. Mais cette solution est incorrecte.
Pourquoi l'approche gourmande ne fonctionnera pas ?
Considérez un papier de format 6x7 alors si nous essayons de couper le papier avec avidité, nous obtiendrons 7 carrés : 1 carré de taille 6x6 et 6 carrés de taille 1x1 alors que la bonne solution est : 5. Par conséquent, une approche gourmande ne fonctionnera pas.
[Approche incorrecte 2] Utilisation de la programmation dynamique
Programmation dynamique avec coupes verticales ou horizontales : Une autre solution qui peut sembler correcte consiste à utiliser Programmation dynamique . Nous pouvons maintenir une table dp[][] telle que dp[i][j] = nombre minimum de carrés pouvant être découpés dans du papier de taille je xj . Puis pour du papier de format axb
- On peut essayer de le couper le long de chaque rangée : dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) où k peut être compris entre [1 i - 1].
- On peut essayer de le découper le long de chaque colonne : dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) où k peut être compris entre [1 j - 1].
Finalement, le minimum de toutes les coupes sera la réponse. Mais cette solution est également incorrecte.
Pourquoi couper verticalement ou horizontalement avec l'approche de programmation dynamique ne fonctionnera pas ?
Cela ne fonctionnera pas car nous supposons qu'une coupe verticale ou horizontale divisera toujours le rectangle en deux parties. Considérez un papier de format 13x11 alors si nous essayons de couper le papier en utilisant l'approche DP, nous obtiendrons 8 carrés mais la bonne réponse (comme indiqué dans les exemples) est 6. Par conséquent, la programmation dynamique ne fonctionnera pas.
[Approche correcte] Utilisation de DFS et de la programmation dynamique
C++Le idée consiste à découper tout le papier à l'aide DFS dans de bas en haut manière. À chaque étape, trouvez le coin le plus bas à gauche du papier et essayez de découper des carrés de toutes les tailles possibles à partir de ce coin. Après avoir découpé à nouveau un carré, trouvez le coin le plus bas à gauche du papier restant pour découper des carrés de toutes les tailles possibles et ainsi de suite. Mais si nous essayions toutes les coupes possibles à partir du coin inférieur gauche de chaque format de papier possible, cela serait tout à fait inefficace. Nous pouvons l'optimiser en utilisant Programmation dynamique pour stocker des coupes minimales pour chaque format de papier possible.
Pour identifier de manière unique n'importe quel format de papier, nous pouvons conserver un tableau remSq[] tel que remSq[i] stocke le nombre de carrés restants de taille 1x1 dans la ième colonne du papier. Donc pour un papier de taille 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Également pour trouver le coin le plus bas à gauche, nous trouverons le premier index ayant le maximum de carrés restants. Nous pouvons donc hacher la valeur du tableau remSq[] pour trouver une clé unique pour toutes les valeurs possibles du tableau remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Sortir
6
Complexité temporelle : O(a^b) pour chacune des b colonnes, nous pouvons avoir des carrés.
Espace auxiliaire : O(a^b) en raison de la mémorisation stockant chaque état unique.

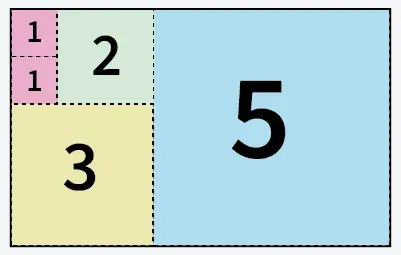 5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 5 X 8
5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 5 X 8 6 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 13 X 11
6 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 13 X 11 5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 6 X 7
5 carrés découpés dans du papier de format 6 X 7