Comment fonctionnent les cookies ?
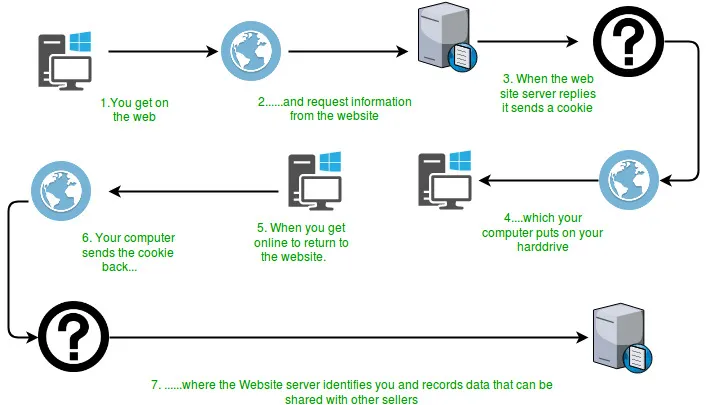 Comme le montre le diagramme ci-dessus, lorsqu'un utilisateur demande pour la première fois une page, le serveur, avec la ressource, envoie un objet cookie à stocker sur la machine du client. Cet objet peut contenir des détails sur la demande. Désormais, plus tard, si l'utilisateur demande à nouveau la même ressource, il envoie avec la demande le cookie stocké qui peut être utilisé par les serveurs pour améliorer encore l'expérience de l'utilisateur. Attributs du Cookie :
Comme le montre le diagramme ci-dessus, lorsqu'un utilisateur demande pour la première fois une page, le serveur, avec la ressource, envoie un objet cookie à stocker sur la machine du client. Cet objet peut contenir des détails sur la demande. Désormais, plus tard, si l'utilisateur demande à nouveau la même ressource, il envoie avec la demande le cookie stocké qui peut être utilisé par les serveurs pour améliorer encore l'expérience de l'utilisateur. Attributs du Cookie : - Tout d'abord, la servlet définit un cookie portant le nom test_cookie. D'autres lignes du programme définissent les attributs du cookie tels que la valeur maximale du domaine d'âge, etc.
- Deuxièmement, la servlet utilise request.getCookies pour rechercher tous les cookies entrants et afficher leurs noms et autres attributs correspondants.
- Si aucun cookie n'est trouvé comme c'est le cas lors de la première demande, un simple message d'affichage s'affiche indiquant qu'il s'agit de la première visite de la page.
Set-Cookie:session-id = 187-4969589-3049309
Set-Cookie: user = geek ;Domain =.foo.example.com
Set-Cookie: user = geek; Path =/ restricted
Set-Cookie: user = geek; expires = Wed 21-Feb-2017 15:23:00 IST
Set-Cookie: user = 'geek'; Max-Age = 3600Constructeur : Creates a cookie with specified name-value pair.
Syntax : public Cookie(String name String value) Parameters : name : name of the cookie value : value associated with this cookieMéthodes :
Syntax : public void setDomain(String pattern) Parameters : pattern : string representing the domain in which this cookie is visible.
Syntax : public String getDomain()
Syntax : public void setComment(String purpose) Parameters : purpose : string representing the purpose of this cookie.
Syntax : public String getComment()
Syntax : public void setMaxAge(long time) Parameters : time : time in seconds before this cookie expires
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setPath(String path) Parameters : path : path where this cookie is returned
Syntax : public String getMaxAge()
Syntax : public void setSecure(boolean secure) Parameters: secure - If true the cookie can only be sent over a secure protocol like https. If false it can be sent over any protocol.
Syntax : public boolean getSecure()
Syntax : public String getName()
Syntax : public void setValue(String newValue) Parameters : newValue - a String specifying the new value
Syntax : public String getValue()
Syntax : public int getVersion()
Syntax : public void setVersion(int v) Parameters : v - 0 for original Netscape specification; 1 for RFC 2965/2109
Syntax : public Cookie clone()Below is a Java implementation of a simple servlet program which stores a cookie in the browser when user first requests for it and then for further requests it displays the cookies stored. Java
// Java program to illustrate methods // of Cookie class import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.Cookie; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * Servlet implementation class cookieTest */ @WebServlet('/cookieTest') public class cookieTest extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public cookieTest() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { response.setContentType('text/html'); // Create a new cookie with the name test cookie // and value 123 Cookie cookie = new Cookie('test_cookie' '123'); // setComment() method cookie.setComment('Just for testing'); // setDomain() method // cookie.setDomain('domain'); // setMaxAge() method cookie.setMaxAge(3600); // setPath() method cookie.setPath('/articles'); // setSecure() method cookie.setSecure(false); // setValue() method cookie.setValue('321'); // setVersion() method cookie.setVersion(0); response.addCookie(cookie); PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter(); pw.print(' '); Cookie ck[] = request.getCookies(); if (ck == null) { pw.print('This is first time the page is requested.
'); pw.print('And therefore no cookies found
'); } else { pw.print('Welcome Again...Cookies found
'); for (int i = 0; i < ck.length; i++) { // getName() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getName() + ''); // getValue() method pw.print('Value :'
+ ck[i].getValue() + ''); // getDomain() method pw.print('Domain :'
+ ck[i].getDomain() + ''); // getPath() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getPath() + ''); // getMaxAge() method pw.print('Max Age :'
+ ck[i].getMaxAge() + ''); // getComment() method pw.print('Comment :'
+ ck[i].getComment() + ''); // getSecure() method pw.print('Name :'
+ ck[i].getSecure() + ''); // getVersion() method pw.print('Version :'
+ ck[i].getVersion() + ''); } pw.print(' '); } pw.close(); } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException IOException { doGet(request response); } }
This is first time the page is requested. And therefore no cookies found.Pour la deuxième demande :
Welcome Again...Cookies found Name :test_cookie Value :321 Domain :null Name :null Max Age :-1 Comment :null Name :false Version :0
Comment exécuter le programme ci-dessus ?
Assurez-vous d’abord qu’un serveur comme Apache Tomcat est installé et configuré avec l’outil que vous utilisez comme Eclipse. Exécutez simplement le programme ci-dessus sur le serveur ou sur votre navigateur local en mettant l'adresse complète du répertoire du serveur que vous utilisez. La servlet CookieTest est une servlet qui effectue trois tâches :