Compte tenu d'un arbre binaire spécial dont nœuds feuilles sont reliés pour former un liste circulaire doublement chaînée la tâche est de trouver le hauteur de l'arbre.
Exemples :
le pivot du panda
Saisir:

Sortir: 2
Explication: La hauteur de l'arbre binaire après reconnaissance des nœuds feuilles est de 2. Dans l'arbre binaire ci-dessus, 6, 5 et 4 sont des nœuds feuilles et forment une liste circulaire doublement chaînée. Ici, le pointeur gauche du nœud feuille agira comme un pointeur précédent de la liste circulaire doublement liée et son pointeur droit agira comme le pointeur suivant de la liste circulaire doublement liée.Saisir:
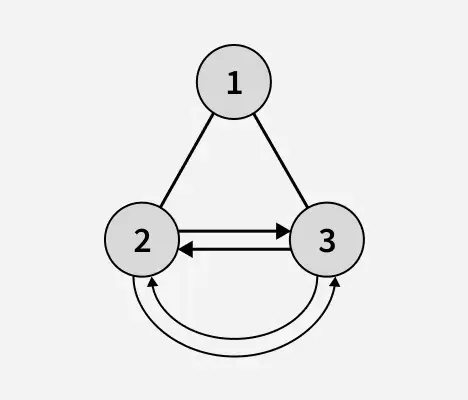
Sortir: 1
Explication: La hauteur de l'arbre binaire après avoir reconnu les nœuds feuilles est de 1. Dans l'arbre binaire ci-dessus, 2 et 3 sont des nœuds feuilles et forment une liste circulaire doublement chaînée.tableau java à lister
Approche :
qu'est-ce que SVN Checkout
C++L'idée est de suivre approche similaire comme nous le faisons pour trouver la hauteur d'un arbre binaire normal . Nous récursivement calculer hauteur de gauche et droite sous-arbres d'un nœud et attribuer hauteur au nœud comme maximum de la taille de deux enfants plus 1. Mais l'enfant gauche et droit d'un nœud feuille sont nuls pour les arbres binaires normaux. Mais ici, le nœud feuille est un nœud de liste circulaire doublement chaîné. Donc pour qu'un nœud soit un nœud feuille, nous vérifions si la gauche du nœud est la droite pointe vers le nœud et son la droite est la gauche pointe également du doigt le nœud lui-même.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; System.out.println(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
# Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf(node): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return (node.left and node.left.right == node and node.right and node.right.left == node) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight(node): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None: return -1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf(node): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.left.left.left = Node(6) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root.left.left.left l2 = root.left.right l3 = root.right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2 l2.right = l3 l3.right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2 l2.left = l1 l1.left = l3 print(findTreeHeight(root))
// C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.Max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; Console.WriteLine(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
// JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf(node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left && node.left.right === node && node.right && node.right.left === node; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight(node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node === null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root.left.left.left; const l2 = root.left.right; const l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; console.log(findTreeHeight(root));
Sortir
3
Complexité temporelle : O(n) où n est le nombre de nœuds.
Espace auxiliaire : Oh)


