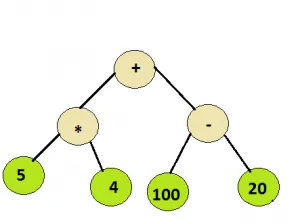
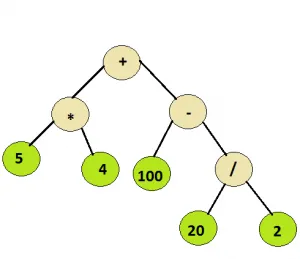
Étant donné un simple arbre d'expression composé d'opérateurs binaires de base, c'est-à-dire + - * et / et de quelques entiers évaluent l'arbre d'expression.
Exemples :
Pratique recommandée Arbre d'expression Essayez-le !Saisir: Nœud racine de l'arborescence ci-dessous
Sortir: 100
Saisir: Nœud racine de l'arborescence ci-dessous
la chaîne est vide
Sortir: 110
Approche: L’approche pour résoudre ce problème est basée sur l’observation suivante :
Comme tous les opérateurs de l'arborescence sont binaires, chaque nœud aura 0 ou 2 enfants. Comme on peut le déduire des exemples ci-dessus, toutes les valeurs entières apparaîtraient au niveau des nœuds feuilles tandis que les nœuds intérieurs représenteraient les opérateurs.
On peut donc faire parcours dans l'ordre de l'arbre binaire et évaluez l'expression à mesure que nous avançons.
Pour évaluer l'arbre syntaxique, une approche récursive peut être suivie.
Algorithme:
- Soit t l'arbre syntaxique
- Si t n'est pas nul, alors
- Si t.info est l'opérande alors
- Retourner t.info
- Autre
- A = résoudre (t.gauche)
- B = résoudre (t.right)
- retourner un opérateur B où l'opérateur est l'information contenue dans t
Vous trouverez ci-dessous la mise en œuvre de l’approche ci-dessus :
C++// C++ program to evaluate an expression tree #include
// Java program to evaluate expression tree import java.lang.*; class GFG{ Node root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public static class Node { String data; Node left right; Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)s.charAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)(s.charAt(i)) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by Ankit Gupta
# Python program to evaluate expression tree # Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node: def __init__(self value): self.left = None self.data = value self.right = None # This function receives a node of the syntax tree # and recursively evaluate it def evaluateExpressionTree(root): # empty tree if root is None: return 0 # leaf node if root.left is None and root.right is None: return int(root.data) # evaluate left tree left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.left) # evaluate right tree right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.right) # check which operation to apply if root.data == '+': return left_sum + right_sum elif root.data == '-': return left_sum - right_sum elif root.data == '*': return left_sum * right_sum else: return left_sum // right_sum # Driver function to test above problem if __name__ == '__main__': # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('-4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('20') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) root = None # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('/') root.right.right.left = node('20') root.right.right.right = node('2') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) # This code is contributed by Harshit Sidhwa
// C# program to evaluate expression tree using System; public class GFG { // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public class Node { public String data; public Node left right; public Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s[0] != '-') for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) s[i] - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (int i = 1; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) (s[i]) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.Equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616
<script> // javascript program to evaluate expression tree var root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function toInt( s) { var num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for (i = 0; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + ( s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (i = 1; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + (s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it function evalTree(root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree var leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree var rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data === ('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data === ('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data === ('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code // Creating a sample tree var root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); document.write(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); document.write('
'+evalTree(root)); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 </script>
Sortir
60 110
Complexité temporelle : O(n) car chaque nœud est visité une fois.
Espace auxiliaire : Sur)