Java fournit deux bibliothèques très puissantes pour travailler avec les données JSON, à savoir : JACKSON et Gson bibliothèques. Nous devons souvent convertir les réponses JSON en une carte pour travailler facilement avec les données JSON renvoyées.
Nous pouvons facilement convertir les données JSON en carte car le format JSON est essentiellement un regroupement de paires clé-valeur et la carte stocke également les données dans des paires clé-valeur.
Comprenons comment nous pouvons utiliser les bibliothèques JACKSON et Gson pour convertir les données JSON en une carte. Nous comprenons également comment utiliser les deux bibliothèques pour convertir les données cartographiques en JSON.
Supposons que nous ayons un fichier Sample.json dans le système qui contient les données suivantes :
{ 'Name' : 'Donal', 'Mobile' : '89346724', 'Designation' : 'Sr. Salesforce Developer', 'Pet' : 'Dog', 'Address' : 'AMERICA' } Bibliothèque JACKSON
Afin de convertir les données JSON en Java Map, nous utilisons l'aide de la bibliothèque JACKSON. Nous ajoutons la dépendance suivante dans le fichier POM.xml pour travailler avec la bibliothèque JACKSON.
com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind 2.5.3
Implémentons la logique de conversion des données JSON en une carte à l'aide des classes ObjectMapper, File et TypeReference.
JacksonConvertJSONToMap.java
// import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; // for reading file data import java.util.Map; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; // create JacksonConvertJSONToMap class to convert JSON data into Java Map public class JacksonConvertJSONToMap { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create instance of the ObjectMapper class to map JSON data ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // create instance of the File class File fileObj = new File('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'); // use try-catch block to convert JSON data into Map try { // read JSON data from file using fileObj and map it using ObjectMapper and TypeReference classes Map userData = mapper.readValue( fileObj, new TypeReference<map>() { }); // print all key-value pairs System.out.println('Name : ' + userData.get('Name')); System.out.println('Mobile : ' + userData.get('Mobile')); System.out.println('Designation : ' + userData.get('Designation')); System.out.println('Pet : ' + userData.get('Pet')); System.out.println('Address : ' + userData.get('Address')); } catch (Exception e) { // show error message e.printStackTrace(); } } } </map> Sortir:
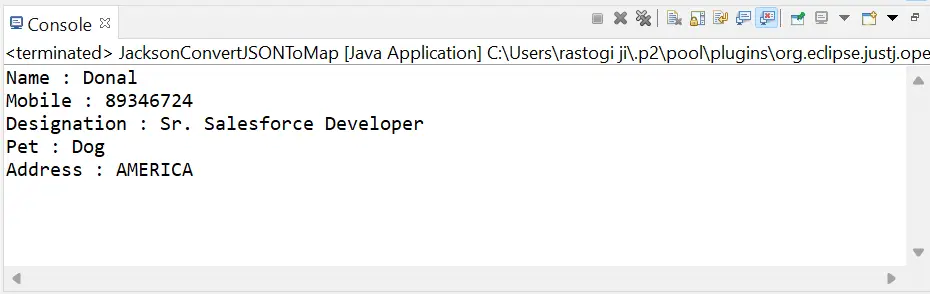
Prenons un autre exemple de la bibliothèque Jackson pour comprendre comment convertir une carte Java en JSON, car nous devons souvent transmettre les données cartographiques à l'API au format JSON. Ainsi, dans cet exemple, nous convertissons les données cartographiques en JSON et les stockons dans un fichier.
JacksonConvertMapToJson.java
// import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; //create JacksonConvertMapToJSON class to convert Map data into JSON public class JacksonConvertMapToJSON { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create instance of the ObjectMapper class ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // declare and initialize map (key is of type String and value is of type Object) Map userData = new HashMap(); // declare variables and array to store user entered data String name, price, model; String colors[]; // create an instance of the Scanner class Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take inputs from the user and store them to the variables System.out.println('Enter the name of the car: '); name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the modal number of the car: '); model = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the price of the car: '); price = sc.nextLine(); colors = new String[3]; colors[0] = 'Red'; colors[1] = 'Black'; colors[2] = 'White'; // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // fill userData map userData.put('Car', name); userData.put('Price', price); userData.put('Model', model); userData.put('Colors', colors); // use try-catch block to convert Java map into JSON try { // use ObjectMapper class to convert Map data into JSON and write it into Sample.json file mapper.writeValue(new File('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'), userData); System.out.println('Map data successfully written to the Sample.json file.'); } catch (Exception e) { // handle exception e.printStackTrace(); } } } Sortir:


Bibliothèque Gson
Gson library est une autre bibliothèque que nous pouvons utiliser pour convertir des données JSON en carte ou des données cartographiques en JSON. Afin d'utiliser la bibliothèque Gson, nous devons ajouter la dépendance suivante dans notre fichier POM.xml.
com.google.code.gson gson 2.8.3
GsonConvertJSONToMap.java
//import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; //create GsonConvertJSONToMap class to convert JSON data into Java Map public class GsonConvertJSONToMap { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // create variable loc that store location of the Sample.json file String loc = 'C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json'; String result; try { // read byte data from the Sample.json file and convert it into String result = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(loc))); // store string data into Map by using TypeToken class Map userData = new Gson().fromJson(result, new TypeToken<hashmap>() { }.getType()); // print all key-value pairs System.out.println('Name : ' + userData.get('Name')); System.out.println('Mobile : ' + userData.get('Mobile')); System.out.println('Designation : ' + userData.get('Designation')); System.out.println('Pet : ' + userData.get('Pet')); System.out.println('Address : ' + userData.get('Address')); } catch (IOException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } } } </hashmap> Sortir:

Prenons un autre exemple de la bibliothèque Gson pour comprendre comment convertir une map Java en JSON. L'utilisation de la bibliothèque Gson est un peu différente de la bibliothèque Jackson.
GsonConvertMapToJson.java
//import required classes and packages package javaTpoint.JavaExample; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import com.google.gson.Gson; //create GsonConvertMapToJson class to convert Map data into JSON public class GsonConvertMapToJson { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare and initialize map(key is of type String and value is of type Object) Map userData = new HashMap(); // declare variables and array to store user entered data String name, price, model; String colors[]; // create an instance of the Scanner class Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take inputs from the user and store them to the variables System.out.println('Enter the name of the car: '); name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the modal number of the car: '); model = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter the price of the car: '); price = sc.nextLine(); colors = new String[3]; colors[0] = 'Red'; colors[1] = 'Black'; colors[2] = 'White'; // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // fill userData map userData.put('Car', name); userData.put('Price', price); userData.put('Model', model); userData.put('Colors', colors); // use try-catch block to convert Java map into JSON try (FileWriter file = new FileWriter('C:\Users\rastogi ji\OneDrive\Desktop\Sample.json')) { // create instance of the Gson Gson gsonObj = new Gson(); // convert userData map to json string String jsonStr = gsonObj.toJson(userData); // use write() of File to write json string into file file.write(jsonStr); // use flush() method to flushes stream file.flush(); System.out.println('Map data successfully written to the Sample.json file.'); } catch (IOException e) { // error handling and exceptions e.printStackTrace(); } } } Sortir:


