Étant donné une matrice rectangulaire mat[][] où certaines cellules contiennent des mines terrestres (notées par 0) et les autres sont sûres (notées par 1), trouvez la longueur du chemin sûr le plus court entre n'importe quelle cellule de la première colonne et n'importe quelle cellule de la dernière colonne.
- Les mines terrestres ne sont pas sûres et leurs quatre cellules adjacentes (en haut, en bas, à gauche et à droite) le sont également.
- Seuls les déplacements horizontaux et verticaux vers des cellules sécurisées adjacentes sont autorisés.
- S'il est impossible d'atteindre la dernière colonne en toute sécurité, renvoyez -1.
Exemples :
comment savoir si quelqu'un vous a bloqué sur Android
Saisir:
avec[][] = [ [1 0 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 0 1]
[1 1 1 1 0] ]
Sortir: 6
Explication:
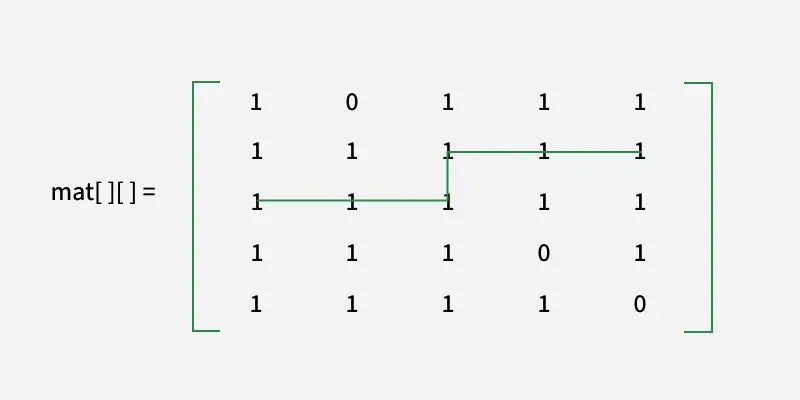
Nous pouvons voir cette longueur la plus courte
l'itinéraire sûr est le 6.
Saisir:
avec[][] = [ [1 1 1 1 1]
[1 1 0 1 1]
[1 1 1 1 1] ]
Sortir: -1
Explication: Il n'y a aucun chemin possible depuis
première colonne à la dernière colonne.
Table des matières
- [Approche] Utiliser le retour en arrière
- [Approche optimisée] Utilisation de la recherche en largeur d'abord
[Approche] Utiliser le retour en arrière
C++L'idée est d'utiliser Retour en arrière . Nous marquons d’abord toutes les cellules adjacentes des mines terrestres comme dangereuses. Ensuite, pour chaque cellule sûre de la première colonne de la matrice, nous avançons dans toutes les directions autorisées et vérifions récursivement si elles mènent à la destination ou non. Si la destination est trouvée, nous mettons à jour la valeur du chemin le plus court, sinon si aucune des solutions ci-dessus ne fonctionne, nous renvoyons false à partir de notre fonction.
#include
import java.util.Arrays; class Solution { // Function to mark unsafe cells (landmines and their adjacent cells) private void markUnsafeCells(int[][] mat) { int r = mat.length; int c = mat[0].length; int[] row = {-1 1 0 0}; int[] col = {0 0 -1 1}; // Create a copy to avoid modifying original safe cells prematurely int[][] temp = new int[r][c]; for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) { temp[i][j] = mat[i][j]; } } // Mark adjacent cells of landmines (0) as unsafe (0) for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) { if (temp[i][j] == 0) { for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + row[k]; int nj = j + col[k]; if (ni >= 0 && ni < r && nj >= 0 && nj < c) { mat[ni][nj] = 0; } } } } } } // DFS to find shortest path from (i j) to any cell in last column private int dfs(int[][] mat boolean[][] visited int i int j int c) { int r = mat.length; // If out of bounds blocked or visited if (i < 0 || i >= r || j < 0 || j >= c || mat[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j]) { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } if (j == c - 1) { return 1; } visited[i][j] = true; int[] row = {-1 1 0 0}; int[] col = {0 0 -1 1}; int minPath = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Try all four directions for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + row[k]; int nj = j + col[k]; int pathLength = dfs(mat visited ni nj c); if (pathLength != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { minPath = Math.min(minPath 1 + pathLength); } } // Backtrack - unmark current cell visited[i][j] = false; return minPath; } public int findShortestPath(int[][] mat) { int r = mat.length; int c = mat[0].length; // Mark all adjacent cells of landmines as unsafe markUnsafeCells(mat); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[r][c]; int minPath = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Try starting from each safe cell in the first column for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { if (mat[i][0] == 1) { int pathLength = dfs(mat visited i 0 c); if (pathLength != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { minPath = Math.min(minPath pathLength); } } } return minPath == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : minPath; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { {1 0 1 1 1} {1 1 1 1 1} {1 1 1 1 1} {1 1 1 0 1} {1 1 1 1 0} }; Solution solution = new Solution(); int result = solution.findShortestPath(mat); System.out.println(result); } }
# Function to mark unsafe cells (landmines and their adjacent cells) def mark_unsafe_cells(mat): r = len(mat) c = len(mat[0]) # Directions for adjacent cells: up down left right row = [-1 1 0 0] col = [0 0 -1 1] # Create a copy to avoid modifying original safe cells prematurely temp = [row[:] for row in mat] # Mark adjacent cells of landmines (0) as unsafe (0) for i in range(r): for j in range(c): if temp[i][j] == 0: for k in range(4): ni = i + row[k] nj = j + col[k] if 0 <= ni < r and 0 <= nj < c: mat[ni][nj] = 0 # DFS to find shortest path from (i j) to any cell in last column def dfs(mat visited i j c): r = len(mat) # If out of bounds blocked or visited if i < 0 or i >= r or j < 0 or j >= c or mat[i][j] == 0 or visited[i][j]: return float('inf') if j == c - 1: return 1 visited[i][j] = True # Four possible moves: up down left right row = [-1 1 0 0] col = [0 0 -1 1] min_path = float('inf') # Try all four directions for k in range(4): ni = i + row[k] nj = j + col[k] path_length = dfs(mat visited ni nj c) if path_length != float('inf'): min_path = min(min_path 1 + path_length) # Backtrack - unmark current cell visited[i][j] = False return min_path def findShortestPath(mat): r = len(mat) c = len(mat[0]) # Mark all adjacent cells of landmines as unsafe mark_unsafe_cells(mat) visited = [[False] * c for _ in range(r)] min_path = float('inf') # Try starting from each safe cell in the first column for i in range(r): if mat[i][0] == 1: path_length = dfs(mat visited i 0 c) if path_length != float('inf'): min_path = min(min_path path_length) return -1 if min_path == float('inf') else min_path def main(): mat = [ [1 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [1 1 1 1 0] ] result = findShortestPath(mat) print(result) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
using System; class GFG { // Function to mark unsafe cells (landmines and their adjacent cells) private void MarkUnsafeCells(int[][] mat) { int r = mat.Length; int c = mat[0].Length; // Directions for adjacent cells: up down left right int[] row = { -1 1 0 0 }; int[] col = { 0 0 -1 1 }; // Create a copy to avoid modifying original safe cells prematurely int[][] temp = new int[r][]; for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { temp[i] = new int[c]; Array.Copy(mat[i] temp[i] c); } // Mark adjacent cells of landmines (0) as unsafe (0) for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) { if (temp[i][j] == 0) { for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + row[k]; int nj = j + col[k]; if (ni >= 0 && ni < r && nj >= 0 && nj < c) { mat[ni][nj] = 0; } } } } } } // DFS to find shortest path from (i j) to any cell in last column private int Dfs(int[][] mat bool[][] visited int i int j int c) { int r = mat.Length; // If out of bounds blocked or visited if (i < 0 || i >= r || j < 0 || j >= c || mat[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j]) { return int.MaxValue; } if (j == c - 1) { return 1; } visited[i][j] = true; int[] row = { -1 1 0 0 }; int[] col = { 0 0 -1 1 }; int minPath = int.MaxValue; // Try all four directions for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + row[k]; int nj = j + col[k]; int pathLength = Dfs(mat visited ni nj c); if (pathLength != int.MaxValue) { minPath = Math.Min(minPath 1 + pathLength); } } // Backtrack - unmark current cell visited[i][j] = false; return minPath; } public int FindShortestPath(int[][] mat) { int r = mat.Length; int c = mat[0].Length; // Mark all adjacent cells of landmines as unsafe MarkUnsafeCells(mat); bool[][] visited = new bool[r][]; for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { visited[i] = new bool[c]; } int minPath = int.MaxValue; // Try starting from each safe cell in the first column for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { if (mat[i][0] == 1) { int pathLength = Dfs(mat visited i 0 c); if (pathLength != int.MaxValue) { minPath = Math.Min(minPath pathLength); } } } return minPath == int.MaxValue ? -1 : minPath; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[][] mat = new int[][] { new int[] { 1 0 1 1 1 } new int[] { 1 1 1 1 1 } new int[] { 1 1 1 1 1 } new int[] { 1 1 1 0 1 } new int[] { 1 1 1 1 0 } }; GFG solution = new GFG(); int result = solution.FindShortestPath(mat); Console.WriteLine(result); } }
function markUnsafeCells(mat) { const r = mat.length; const c = mat[0].length; // Directions for adjacent cells: up down left right const row = [-1 1 0 0]; const col = [0 0 -1 1]; // Create a copy to avoid modifying original safe cells prematurely const temp = mat.map(row => [...row]); // Mark adjacent cells of landmines (0) as unsafe (0) for (let i = 0; i < r; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < c; j++) { if (temp[i][j] === 0) { for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { const ni = i + row[k]; const nj = j + col[k]; if (ni >= 0 && ni < r && nj >= 0 && nj < c) { mat[ni][nj] = 0; } } } } } } function dfs(mat visited i j c) { const r = mat.length; // If out of bounds blocked or visited if (i < 0 || i >= r || j < 0 || j >= c || mat[i][j] === 0 || visited[i][j]) { return Infinity; } // If reached the last column if (j === c - 1) { return 1; } visited[i][j] = true; const row = [-1 1 0 0]; const col = [0 0 -1 1]; let minPath = Infinity; // Try all four directions for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { const ni = i + row[k]; const nj = j + col[k]; const pathLength = dfs(mat visited ni nj c); if (pathLength !== Infinity) { minPath = Math.min(minPath 1 + pathLength); } } // Backtrack - unmark current cell visited[i][j] = false; return minPath; } function findShortestPath(mat) { const r = mat.length; const c = mat[0].length; // Mark all adjacent cells of landmines as unsafe markUnsafeCells(mat); const visited = Array(r).fill().map(() => Array(c).fill(false)); let minPath = Infinity; // Try starting from each safe cell in the first column for (let i = 0; i < r; i++) { if (mat[i][0] === 1) { const pathLength = dfs(mat visited i 0 c); if (pathLength !== Infinity) { minPath = Math.min(minPath pathLength); } } } return minPath === Infinity ? -1 : minPath; } const mat = [ [1 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [1 1 1 1 0] ]; const result = findShortestPath(mat); console.log(result);
Sortir
6
Complexité temporelle : O(4^(r * c)) où r est le nombre de lignes et c le nombre de colonnes dans la matrice donnée.
Espace auxiliaire : O(r*c) car nous utilisons un espace supplémentaire comme visted[r][c].
type de date dactylographié
[Approche optimisée] Utilisation de la recherche en largeur d'abord
C++Il peut être résolu en temps polynomial à l’aide de la recherche en largeur. Mettez en file d'attente toutes les cellules sûres de la dernière colonne dans la file d'attente avec une distance = 1. Au fur et à mesure que BFS avance, le chemin le plus court vers chaque cellule de la dernière colonne est calculé. Enfin, parmi toutes les cellules accessibles de la première colonne, indiquez la distance minimale.
#include
import java.util.*; public class Solution { static int[] rowNum = {-1 0 0 1}; static int[] colNum = {0 -1 1 0}; public static int findShortestPath(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); int[][] d = new int[n][m]; // Initializing distance array with large values for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Arrays.fill(d[i] (int) 1e9); } // Lambda-like helper function: check if cell is valid java.util.function.BiFunction<Integer Integer Boolean> isValid = (i j) -> { return !(i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m); }; // Helper function: check if cell and adjacent cells are safe java.util.function.BiFunction<Integer Integer Boolean> check = (i j) -> { if (!isValid.apply(i j)) return false; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + rowNum[k]; int nj = j + colNum[k]; if (isValid.apply(ni nj) && mat[ni][nj] == 0) return false; } return true; }; // Pushing cells from the rightmost column into the queue for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (check.apply(i m - 1)) { q.add(new int[]{i m - 1 1}); } } // BFS traversal while (!q.isEmpty()) { int[] z = q.poll(); int x = z[0] y = z[1] dis = z[2]; if (d[x][y] > dis) { d[x][y] = dis; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = x + rowNum[k]; int nj = y + colNum[k]; if (check.apply(ni nj)) { q.add(new int[]{ni nj dis + 1}); } } } } // Finding the minimum distance in the first column int ans = (int) 1e9; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans = Math.min(ans d[i][0]); } // If no safe path found return -1 if (ans >= 1e9) ans = -1; return ans; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { {1 0 1 1 1} {1 1 1 1 1} {1 1 1 1 1} {1 1 1 0 1} {1 1 1 1 0} }; int result = findShortestPath(mat); System.out.println(result); } }
from collections import deque rowNum = [-1 0 0 1] colNum = [0 -1 1 0] def findShortestPath(mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) q = deque() d = [[10**9 for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)] # Check if cell is valid def isValid(i j): return not (i < 0 or i >= n or j < 0 or j >= m) # Check if cell and its adjacent cells are safe def check(i j): if not isValid(i j): return False for k in range(4): ni nj = i + rowNum[k] j + colNum[k] if isValid(ni nj) and mat[ni][nj] == 0: return False return True # Pushing cells from the rightmost column into the queue for i in range(n): if check(i m - 1): q.append((i m - 1 1)) # BFS traversal while q: x y dis = q.popleft() if d[x][y] > dis: d[x][y] = dis for k in range(4): ni nj = x + rowNum[k] y + colNum[k] if check(ni nj): q.append((ni nj dis + 1)) # Finding the minimum distance in the first column ans = min(d[i][0] for i in range(n)) # If no safe path found return -1 if ans >= 10**9: ans = -1 return ans if __name__ == '__main__': mat = [ [1 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [1 1 1 1 0] ] result = findShortestPath(mat) print(result)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Solution { static int[] rowNum = { -1 0 0 1 }; static int[] colNum = { 0 -1 1 0 }; // Check if cell is valid static bool IsValid(int i int j int n int m) { return !(i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m); } // Check if cell and its adjacent cells are safe static bool Check(int i int j int[][] mat int n int m) { if (!IsValid(i j n m)) return false; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = i + rowNum[k]; int nj = j + colNum[k]; if (IsValid(ni nj n m) && mat[ni][nj] == 0) return false; } return true; } public static int FindShortestPath(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.Length; int m = mat[0].Length; Queue<(int int int)> q = new Queue<(int int int)>(); int[] d = new int[n m]; // Initialize distance array with large value for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) d[i j] = int.MaxValue / 2; // Push safe cells from rightmost column for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (Check(i m - 1 mat n m)) { q.Enqueue((i m - 1 1)); } } // BFS traversal while (q.Count > 0) { var (x y dis) = q.Dequeue(); if (d[x y] > dis) { d[x y] = dis; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int ni = x + rowNum[k]; int nj = y + colNum[k]; if (Check(ni nj mat n m)) { q.Enqueue((ni nj dis + 1)); } } } } // Find minimum distance in the first column int ans = int.MaxValue / 2; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) ans = Math.Min(ans d[i 0]); return ans >= int.MaxValue / 2 ? -1 : ans; } static void Main() { int[][] mat = new int[][] { new int[] {1 0 1 1 1} new int[] {1 1 1 1 1} new int[] {1 1 1 1 1} new int[] {1 1 1 0 1} new int[] {1 1 1 1 0} }; int result = FindShortestPath(mat); Console.WriteLine(result); } }
function findShortestPath(mat) { const n = mat.length; const m = mat[0].length; const rowNum = [-1 0 0 1]; const colNum = [0 -1 1 0]; // Distance matrix initialized to large value const d = Array.from({ length: n } () => Array(m).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)); // Check if cell is valid function isValid(i j) { return !(i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m); } // Check if cell and its adjacent cells are safe function check(i j) { if (!isValid(i j)) return false; for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { let ni = i + rowNum[k]; let nj = j + colNum[k]; if (isValid(ni nj) && mat[ni][nj] === 0) return false; } return true; } // Queue for BFS let q = []; // Push safe cells from rightmost column for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (check(i m - 1)) { q.push([i m - 1 1]); } } // BFS traversal while (q.length > 0) { let [x y dis] = q.shift(); if (d[x][y] > dis) { d[x][y] = dis; for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { let ni = x + rowNum[k]; let nj = y + colNum[k]; if (check(ni nj)) { q.push([ni nj dis + 1]); } } } } // Find minimum distance in first column let ans = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans = Math.min(ans d[i][0]); } return ans >= Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ? -1 : ans; } const mat = [ [1 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [1 1 1 1 0] ]; const result = findShortestPath(mat); console.log(result);
Sortir
6
Complexité temporelle : O(r * c) où r et c sont respectivement le nombre de lignes et de colonnes dans la matrice donnée.
Espace auxiliaire : O(r*c)
